Substrate-selective small-molecule modulators of enzymes: Mechanisms and opportunities
- PMID: 36455490
- PMCID: PMC9870951
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2022.102231
Substrate-selective small-molecule modulators of enzymes: Mechanisms and opportunities
Abstract
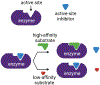
Small-molecule inhibitors of enzymes are widely used tools in reverse chemical genetics to probe biology and explore therapeutic opportunities. They are often compared with genetic knockdown or knockout and are expected to produce phenotypes similar to the genetic perturbations. This review aims to highlight that small molecule inhibitors of enzymes and genetic perturbations may not necessarily produce the same phenotype due to the possibility of substrate-selective or substrate-dependent effects of the inhibitors. Examples of substrate-selective inhibitors and the mechanisms for the substrate-selective effects are discussed. Substrate-selective modulators of enzymes have distinct advantages and cannot be easily replaced with biologics. Thus, they present an exciting opportunity for chemical biologists and medicinal chemists.
Keywords: COX-2; Chemical genetics; Gamma-secretase; Insulin degrading enzyme; Reverse chemical genetics; SIRT2; SIRT6; Sirtuins; Substrate-dependent inhibition; Substrate-selective inhibition.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Hening Lin reports a relationship with Sedec Therapeutics that includes: consulting or advisory and equity or stocks.
Figures

References
-
- Kawasumi M, Nghiem P: Chemical genetics: elucidating biological systems with small-molecule compounds. J Invest Dermatol 2007, 127:1577–1584. - PubMed
-
- Hutzler JM, Kolwankar D, Hummel MA, Tracy TS: Activation of CYP2C9-mediated metabolism by a series of dapsone analogs: kinetics and structural requirements. Drug Metab Dispos 2002, 30:1194–1200. - PubMed
-
- Wang RW, Newton DJ, Liu N, Atkins WM, Lu AY: Human cytochrome P-450 3A4: in vitro drug-drug interaction patterns are substrate-dependent. Drug Metab Dispos 2000, 28:360–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

