Severe myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome in children and young people: a British Paediatric Surveillance Unit study
- PMID: 36456114
- PMCID: PMC9985735
- DOI: 10.1136/archdischild-2022-324319
Severe myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome in children and young people: a British Paediatric Surveillance Unit study
Abstract
Objectives: Primary objective: to determine the point prevalence and incidence rate of severe myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) in children aged 5-16 years over 13 months.
Secondary objectives: to describe the demographic features, symptoms, impact on activities of daily living, school attendance and time to diagnosis.
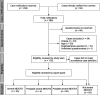
Design: Prospective surveillance study conducted by the British Paediatric Surveillance Unit. Paediatricians was asked if they had assessed a child with severe ME/CFS (screening definition for prevalence and incidence: children (5-16 years) diagnosed with ME/CFS so severe that they are unable to attend school for more than 1 hour a week during the last 6 weeks of the school term).
Participants: Patients 5-16 years of age, seen by paediatricians and two large ME/CFS specialist services across the UK and Ireland.
Outcome measures: Paediatrician-completed questionnaires describing demographics, symptoms, function and treatment, (applying National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE)-recommended criteria to assess severity of ME/CFS). Diagnosis of severe, probable severe or possible severe ME/CFS was made only with evidence of NICE-recommended screening blood tests.
Results: 285 cases were reported, of which of which 33 were severe, 4 probable severe and 55 possible severe. Estimated prevalence was 3.2 per million children (95% CI 2.2 to 4.5). Including possible/probable severe ME/CFS gave 8.9 per million children (95% CI 7.2 to 11). The incidence rate was 0.90 per million children-years (95% CI 0.43 to 1.65) (1.97 per million children-years (95% CI 1.24 to 2.99)). Median age was 13 years and 58% of cases were female. Median time to diagnosis was 0.47 years.
Conclusions: Although the incidence of children presenting with severe ME/CFS is low, all were very disabled. In addition, the majority receive little or no education. Paediatricians need to consider how to provide rehabilitation and education for these disabled young people.
Keywords: child health; chronic fatigue syndrome; paediatrics.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Management of severe ME/CFS in children and young people in the UK: a British Paediatric Surveillance Unit study.BMJ Paediatr Open. 2024 Mar 7;8(1):e002436. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2023-002436. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2024. PMID: 38453418 Free PMC article.
-
What stops children with a chronic illness accessing health care: a mixed methods study in children with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (CFS/ME).BMC Health Serv Res. 2011 Nov 11;11:308. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-11-308. BMC Health Serv Res. 2011. PMID: 22078101 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of FITNET-NHS (Fatigue In Teenagers on the interNET in the NHS) compared to Activity Management to treat paediatric chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS)/myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME): protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2018 Feb 22;19(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2500-3. Trials. 2018. PMID: 29471861 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: an evidence-based approach to diagnosis and management by clinicians.Rev Environ Health. 2015;30(4):223-49. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2015-0026. Rev Environ Health. 2015. PMID: 26613325 Review.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of chronic fatigue syndrome/myalgic encephalomyelitis (CFS/ME).J Transl Med. 2020 Feb 24;18(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02269-0. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32093722 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Management of severe ME/CFS in children and young people in the UK: a British Paediatric Surveillance Unit study.BMJ Paediatr Open. 2024 Mar 7;8(1):e002436. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2023-002436. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2024. PMID: 38453418 Free PMC article.
-
Recent research in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome: an evidence map.Health Technol Assess. 2025 Mar 26:1-78. doi: 10.3310/BTBD8846. Online ahead of print. Health Technol Assess. 2025. PMID: 40162526 Free PMC article.
-
The gastrointestinal microbiota in the development of ME/CFS: a critical view and potential perspectives.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 28;15:1352744. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1352744. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38605969 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- NICE . Chronic fatigue syndrome/myalgic encephalomyelitis (or encephalopathy): diagnosis and management. NG2062021.
-
- Pheby D, Sneddon P, Heinrich I, et al. . Severe ME/CFS in Adults-A report from the CHROME Database. Medical Statistician 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical