Effect of ovarian growth factors on ultra-structural maturation in frozen human immature oocytes after in vitro maturation: a comparative study
- PMID: 36457030
- PMCID: PMC9714011
- DOI: 10.1186/s12978-022-01521-8
Effect of ovarian growth factors on ultra-structural maturation in frozen human immature oocytes after in vitro maturation: a comparative study
Abstract
Background: In artificial reproductive technique (ART), nearly 20% of human oocytes are immature in the germinal vesicle (GV) phase. Consequently, the best method for reserving them is cryopreserving GV oocytes, and in vitro maturation (IVM) is recommended. The aim of this study was to determine the ultrastructure characteristics of fresh and vitrified immature human oocytes after in vitro maturation in conditioned mediums.
Methods: This study was a comparative laboratory study carried out in 2018 at Afzalipur Infertility Center in Kerman. 170 fresh and 198 vitrified GV oocytes were cultured within three IVM mediums; α-mem as control medium, α-mem supplemented with human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) and α-mem supplemented with ovarian growth factors (O.F). After 48 h, the maturation rate and morphological feature of IVM oocytes [132 fresh IVM (fIVM) and 134 vitrified IVM (vIVM)] were evaluated. For the ultrastructure study, 10 IVM oocytes from each medium were compared with 10 fresh in vivo oocytes cancelled from ART.
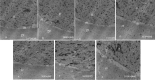
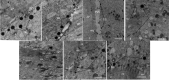
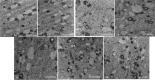
Results: The survival rate of vitrified GV oocyte after thawing was 88.88%. The oocyte maturation rate was reduced in vIVM compared to the fIVM group (76.33% vs. 77.95%); the highest oocyte maturation rate in the O.F fIVM and lowest in α-mem vIVM (82.35% vs. 71.42%). The lowest number of cortical granules was observed in α-mem vIVM, but the greatest presence of M-SER aggregates was in O.F fIVM. In vIVM oocytes, the oolemma contained irregular little microvillus organization.
Conclusions: The O.F mediums have shown the highest maturation which defends the oocyte ultra-structural conservation.
Keywords: In vitro maturation; Infertility; Oocytes; Ovarian growth factors; Ultrastructure.
Plain language summary
In artificial reproductive technique (ART), nearly 20% of human oocytes are immature in the germinal vesicle (GV) phase. Consequently, the best method for reserving them is cryopreserving GV oocytes, and in vitro maturation (IVM) is recommended. This study was a comparative laboratory study carried out in 2018 at Afzalipur Infertility Center in Kerman. 170 fresh and 198 vitrified GV oocytes were cultured within three IVM mediums; α-mem as the control medium, α-mem supplemented with human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs), and α-mem supplemented with ovarian growth factors (O.F). After 48 h, the maturation rate and morphological features of IVM oocytes were evaluated. For the ultrastructure study, 10 IVM oocytes from each medium were compared with 10 fresh in vivo oocytes cancelled from ART. The survival rate of vitrified GV oocytes after thawing was 88.88%. The oocyte maturation rate was reduced in vIVM compared to the fIVM group (76.33% vs. 77.95%); the highest oocyte maturation rate in the O.F fIVM and lowest in α-mem vIVM (82.35% vs. 71.42%). The lowest number of cortical granules was observed in α-mem vIVM, but the greatest presence of M-SER aggregates was in O.F fIVM. In vIVM oocytes, the oolemma contained irregular little microvillus organization. The O.F mediums have shown the highest maturation with defending the oocyte ultra-structural conservation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Modulates Apoptotic and Stress-Related Gene Expression, Ameliorates Maturation and Allows for the Development of Immature Human Oocytes after Artificial Activation.Genes (Basel). 2017 Dec 8;8(12):371. doi: 10.3390/genes8120371. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29292728 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Ovarian Factor Mediums on the Apoptotic Gene Expression and Embryo Quality Derived From Vitrified Immature Human Oocytes.J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2023 Aug;73(4):309-315. doi: 10.1007/s13224-022-01726-8. Epub 2022 Dec 31. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2023. PMID: 37701087 Free PMC article.
-
Maturation capacity, morphology and morphometric assessment of human immature oocytes after vitrification and in-vitro maturation.Iran J Reprod Med. 2011 Summer;9(3):209-16. Iran J Reprod Med. 2011. PMID: 26396566 Free PMC article.
-
Vitrification of human immature oocytes before and after in vitro maturation: a review.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2017 Nov;34(11):1413-1426. doi: 10.1007/s10815-017-1005-4. Epub 2017 Aug 18. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2017. PMID: 28822010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In-vitro maturation of germinal vesicle and metaphase I eggs prior to cryopreservation optimizes reproductive potential in patients undergoing fertility preservation.Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Jun;26(3):168-73. doi: 10.1097/GCO.0000000000000062. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2014. PMID: 24752002 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of different sperm sources on the clinical outcomes of in vitro oocyte maturation cycles combined with intracytoplasmic sperm injection.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 20;14:1115210. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1115210. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36891059 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akbari H. The effect of conditioned media on mouse oocytes ultrastructure following in vitro maturation. Gene Rep. 2020;20:100732. doi: 10.1016/j.genrep.2020.100732. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

