Intra-subject stability of different expressions of spatial QRS-T angle and their relationship to heart rate
- PMID: 36457310
- PMCID: PMC9708109
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.939633
Intra-subject stability of different expressions of spatial QRS-T angle and their relationship to heart rate
Abstract
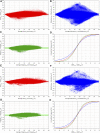
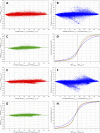
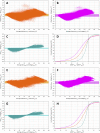
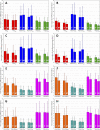
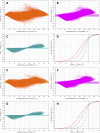
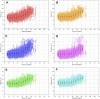
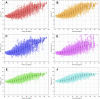
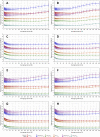
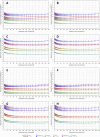
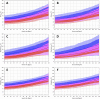
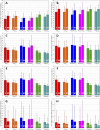
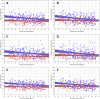
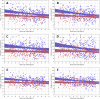
Three-dimensional angle between the QRS complex and T wave vectors is a known powerful cardiovascular risk predictor. Nevertheless, several physiological properties of the angle are unknown or poorly understood. These include, among others, intra-subject profiles and stability of the angle relationship to heart rate, characteristics of angle/heart-rate hysteresis, and the changes of these characteristics with different modes of QRS-T angle calculation. These characteristics were investigated in long-term 12-lead Holter recordings of 523 healthy volunteers (259 females). Three different algorithmic methods for the angle computation were based on maximal vector magnitude of QRS and T wave loops, areas under the QRS complex and T wave curvatures in orthogonal leads, and weighted integration of all QRS and T wave vectors moving around the respective 3-dimensional loops. These methods were applied to orthogonal leads derived either by a uniform conversion matrix or by singular value decomposition (SVD) of the original 12-lead ECG, giving 6 possible ways of expressing the angle. Heart rate hysteresis was assessed using the exponential decay models. All these methods were used to measure the angle in 659,313 representative waveforms of individual 10-s ECG samples and in 7,350,733 individual beats contained in the same 10-s samples. With all measurement methods, the measured angles fitted second-degree polynomial regressions to the underlying heart rate. Independent of the measurement method, the angles were found significantly narrower in females (p < 0.00001) with the differences to males between 10o and 20o, suggesting that in future risk-assessment studies, different angle dichotomies are needed for both sexes. The integrative method combined with SVD leads showed the highest intra-subject reproducibility (p < 0.00001). No reproducible delay between heart rate changes and QRS-T angle changes was found. This was interpreted as a suggestion that the measurement of QRS-T angle might offer direct assessment of cardiac autonomic responsiveness at the ventricular level.
Keywords: ECG measurements; healthy volunteers; heart rate; heart rate hysteresis; long-term ECG; polynomial regression; sex differences; spatial QRS-T angle.
Copyright © 2022 Andršová, Hnatkova, Toman, Šišáková, Smetana, Huster, Barthel, Novotný, Schmidt and Malik.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

