The Effect of Sildenafil on Pregnancy Outcomes in Pregnant Women With Idiopathic Borderline Oligohydramnios: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 36457659
- PMCID: PMC9678853
- DOI: 10.18502/jfrh.v16i2.9482
The Effect of Sildenafil on Pregnancy Outcomes in Pregnant Women With Idiopathic Borderline Oligohydramnios: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
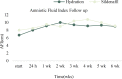
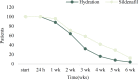
Objective: Borderline oligohydramnios always produces a dilemma of management and counseling among obstetricians. This study was designed to compare the effect of sildenafil plus fluid therapy versus fluid therapy alone on pregnancy outcomes and AFI improvement in pregnant women complicated by idiopathic borderline oligohydramnios. Materials and methods : This randomized clinical trial was conducted in Arash Women's Hospital, Tehran, Iran from 2017 to 2020. Fifty-one pregnant women with idiopathic borderline oligohydramnios were allocated to two groups. Group 1 received fluid therapy and Group 2 received fluid therapy and Sildenafil 25 mg three times daily for six weeks. AFI was measured at the time of randomization, 24 h after treatment and then weekly for six weeks. The changes in AFI, type of delivery, gestational age at delivery, and neonatal outcomes were compared between the two groups. Results: After the intervention, the change in AFI between two groups was not statistically significant. Maternal and fetal outcomes are compared between two groups and there was no significant difference between them. The median (Inter-quartile range) AFI after intervention, in Sildenafil group compared with hydration group, were in 24 hours (8.5 vs. 8, p=0.27), first (9.5 vs. 9.1, p=0.74), second (9 vs 10, p=0.12) third (10.4 vs. 9.4, p=0.33), fourth (10.8 vs 9.1, p=0.1) and Fifth week (10 vs 9.3, p=0.5) of follow-up respectively, but none of them were statistically significant. Conclusion: The findings showed that sildenafil plus fluid therapy do not improve the pregnancy outcomes in women with isolated borderline oligohydramnios compared to fluid therapy alone.
Keywords: Oligohydramnios; Pregnancy Outcome; Sildenafil.
Copyright © 2022 Tehran University of Medical Sciences. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures
References
-
- Rabie N, Magann E, Steelman S, Ounpraseuth S. Oligohydramnios in complicated and uncomplicated pregnancy: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2017;49:442–9. - PubMed
-
- HalaAbd El-fttah A, AliSabahRamadan HA. The effect of oral versus intravenous fluid therapy on maternal and neonatal outcomes for women with oligohydramnios. Egyptian Nursing Jouurnal. 2018;15:228.
-
- Yadav P, Basnet T, Yadav SP. Maternal and perinatal outcome in borderline oligohydramnios: a hospital-based studY. International Journal of Medical Science And Diagnosis. 2021;5:19–21.
-
- Ghafarnejad M, Tehrani MB, Anaraki FB, Mood NI, Nasehi L. Oral hydration therapy in oligohydramnios. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2009;35:895–900. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources