Distribution and frequency of common mutations in rpoB gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis detected by Xpert MTB/RIF and identification of residential areas of rifampicin resistant-TB cases: A first retrospective study from Mizoram, Northeast India
- PMID: 36457842
- PMCID: PMC9707063
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jctube.2022.100342
Distribution and frequency of common mutations in rpoB gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis detected by Xpert MTB/RIF and identification of residential areas of rifampicin resistant-TB cases: A first retrospective study from Mizoram, Northeast India
Abstract
Background: Rifampicin resistance (RR) is a surrogate marker of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. The aim of this study is to determine the frequency of the commonly mutated probes for rpoB gene and locate the residential areas of the Rifampicin Resistant-TB (RR-TB) patients in a high endemic zone of Northeast India.
Methods: Archived data of 13,454 Xpert MTB/RIF reports were evaluated retrospectively between 2014 and 2021. Socio-demographic and available clinical information were reviewed and analyzed for RR-TB cases only. Logistic Regression was used to analyze the parameters with respect to probe types. P-value ≤ 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
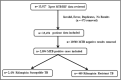
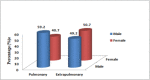
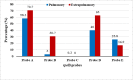
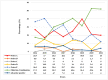
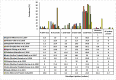
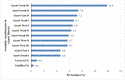
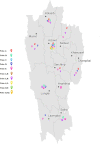
Results: 2,894 patients had Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection out of which 460 were RR-TB, which was most prevalent among 25-34 years. The most common mutation occurred in probe A (25.9 %) followed by E (23.5 %), D (9.8 %), B (2.6 %) and the least in C (0.2 %). High prevalence (34.3 %) of probe mutation combinations were also found: probes AB (0.4 %), AD (32.8 %), AE (0.4 %), DE (0.2 %) and ADE (0.4 %). Seventeen patients (3.7 %) were found without any missing probes. RR-TB patients were mostly located in Aizawl North -III, South -II and East -II constituencies.
Conclusion: This study provides genetic pattern of drug resistance accountable for RR over the past years in Mizoram which will help local clinicians in the initiation of correct treatment. Also, our findings provide a baseline data on the magnitude of RR-TB within the state and identification of the residential areas can help local health authorities in planning surveillance programs to control the spread of RR-TB.
Keywords: Mizoram; Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Northeast India; Probe mutations; Xpert MTB/RIF.
© 2022 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rifampicin resistance mutations in the 81 bp RRDR of rpoB gene in Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates using Xpert® MTB/RIF in Kampala, Uganda: a retrospective study.BMC Infect Dis. 2014 Sep 4;14:481. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-481. BMC Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 25190040 Free PMC article.
-
Rifampicin resistance mutations in the 81 bp RRDR of rpoB gene in Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates using Xpert MTB/RIF in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan: a retrospective study.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 12;16:413. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1745-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27519406 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Missing Probes in rpoB gene in Rifampicin Resistant PTB and EPTB Cases Using Xpert MTB/RIF Assay in Sirmaur, Himachal Pradesh.J Assoc Physicians India. 2020 Nov;68(11):33-36. J Assoc Physicians India. 2020. PMID: 33187034
-
Epidemiology of Rifampicin Resistant Tuberculosis and Common Mutations in rpoB Gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A Retrospective Study from Six Districts of Punjab (India) Using Xpert MTB/RIF Assay.J Lab Physicians. 2016 Jul-Dec;8(2):96-100. doi: 10.4103/0974-2727.180789. J Lab Physicians. 2016. PMID: 27365918 Free PMC article.
-
Does Xpert® MTB/RIF assay give rifampicin resistance results without identified mutation? Review of cases from Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Jan 30;20(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-4817-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32000702 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The pattern of rpoB gene mutation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and predictors of rifampicin resistance detected by GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay in Tanzania.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 26;19(8):e0296563. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296563. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39186753 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Xpert MTB/RIF assay in detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis in samples with different results by smear and culture in a coastal city with high incidence of tuberculosis.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Jan 11;25(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10446-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39799307 Free PMC article.
-
RpoB mutation patterns in Rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis: a Jiangxi Province study, 2021-2023.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 31;15(1):27988. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11949-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40745428 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective epidemiological analysis of pulmonary tuberculosis in the older adult and characterization of rifampicin resistance-associated rpoB mutations in Nantong City, China (2014-2023).Front Public Health. 2025 May 26;13:1577211. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1577211. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40491993 Free PMC article.
-
Factors influencing false-positive results of rifampicin resistance detected by Xpert MTB/RIF: A retrospective study in Zhejiang, China.Heliyon. 2024 May 21;10(11):e31680. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31680. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38841482 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global tuberculosis report 2013. World Health Organization. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/91355.
-
- Global tuberculosis report 2020. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
-
- Global tuberculosis report 2018. World Health Organization; 2018. License: CC BY- NC-SA 3.0 IGO. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/274453.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

