Transcriptome analysis of differentially expressed circRNAs miRNAs and mRNAs during the challenge of coccidiosis
- PMID: 36458003
- PMCID: PMC9706185
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.910860
Transcriptome analysis of differentially expressed circRNAs miRNAs and mRNAs during the challenge of coccidiosis
Abstract
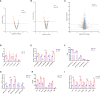
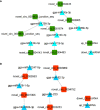
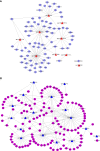
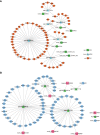
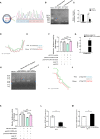
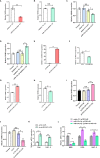
Avian coccidiosis is a common enzootic disease caused by infection of Eimeria species parasites. It causes huge economic losses in the global poultry industry. Current control using anticoccidial drugs or vaccination is limited due to drug resistance and the relatively high cost of vaccines. Improving host genetic resistance to Eimeria species is considered an effective strategy for improved control of coccidiosis. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been found to function as biomarkers or diagnoses of various kinds of diseases. The molecular biological functions of circRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs related to Sasso chicken have not yet been described during Eimeria species challenge. In this study, RNA-seq was used to profile the expression pattern of circRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs in spleens from Eimeria tenella-infected and non-infected commercial dual-purpose Sasso T445 breed chickens. Results showed a total of 40 differentially expressed circRNAs (DEcircRNAs), 31 differentially expressed miRNAs (DEmiRNAs), and 820 differentially expressed genes (DEmRNAs) between infected and non-infected chickens. Regulatory networks were constructed between differentially expressed circRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs to offer insights into the interaction mechanisms between chickens and Eimeria spp. Functional validation of a significantly differentially expressed circRNA, circMGAT5, revealed that circMGAT5 could sponge miR-132c-5p to promote the expression of the miR-132c-5p target gene monocyte to macrophage differentiation-associated (MMD) during the infection of E. tenella sporozoites or LPS stimulation. Pathologically, knockdown of circMGAT5 significantly upregulated the expression of macrophage surface markers and the macrophage activation marker, F4/80 and MHC-II, which indicated that circMGAT5 might inhibit the activation of macrophage. miR-132c-5p markedly facilitated the expression of F4/80 and MHC-II while circMGAT5 could attenuate the increase of F4/80 and MHC-II induced by miR-132c-5p, indicating that circMGAT5 exhibited function through the circMGAT5-miR-132c-5p-MMD axis. Together, our results indicate that circRNAs exhibit their resistance or susceptive roles during E. tenella infection. Among these, circMGAT5 may inhibit the activation of macrophages through the circMGAT5-miR-132c-5p-MMD axis to participate in the immune response induced by Eimeria infection.
Keywords: MMD; avian coccidiosis; circMGAT5; circRNAs; sasso chicken.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Wang, Chen, Akinci, Luo, Xu, Jebessa, Blake, Sparks, Hanotte and Nie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

