Use of 'Printed Investigation Sheet' as Checklist in Admitted Antenatal Patients: A Quality Improvement Initiative
- PMID: 36458072
- PMCID: PMC9568633
- DOI: 10.1007/s13224-022-01630-1
Use of 'Printed Investigation Sheet' as Checklist in Admitted Antenatal Patients: A Quality Improvement Initiative
Abstract
Background: The study was conducted to establish use of printed investigation sheets as checklists for timely workup and clinical evaluation of antenatal women with medical diseases; admitted in maternity ward, by third day of their hospital admission. This was aimed to standardize care, avoid repeated blood sampling of patients, avoid delay in starting the treatment and help teams perform optimally by systematic use of quality improvement (QI) tools.
Methods: The present study was conducted in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology at a tertiary care teaching hospital using point-of-care quality improvement methodology systematically. A QI team was made who formulated an aim statement, conducted a root-cause analysis, performed plan-do-study-act (PDSA) cycles. The outcome was measured as complete clinical evaluation of antenatal women with anaemia, hypertension, and/or diabetes by third day of admission in the maternity ward.
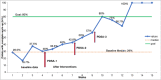
Results: The baseline data showed that median percentage of patients with complete clinical evaluation was only 29.2%. After a root-cause analysis with fishbone tool, three PDSA cycles were conducted to achieve the target of 80%. After the third PDSA cycle, complete clinical evaluation in anaemia, hypertension, diabetes showed an improving trend with a median of 75%.
Conclusion: Adopting simple principles of quality improvement, initiating use of printed investigation sheets as checklist can streamline and expedite clinical evaluation of antenatal patients with medical problems so as to avoid unnecessary delay in initiating the management in busy maternity wards.
Keywords: Antenatal; Checklists; Patient safety; Plan-do-study-act (PDSA) cycle; Printed investigation sheet; Quality improvement; Quality of care; Standardized care.
© Federation of Obstetric & Gynecological Societies of India 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bergman B, Hellström A, Lifvergren S, et al. An emerging science of improvement in health care. Qual Eng. 2015;27(1):17–34. doi: 10.1080/08982112.2015.968042. - DOI
-
- Langley GJ, Moen R, Nolan KM, et al. The improvement guide: a practical approach to enhancing organizational performance. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass; 2009.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
