Enhanced resolution optoacoustic microscopy using a picosecond high repetition rate Q-switched microchip laser
- PMID: 36458112
- PMCID: PMC9705569
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JBO.27.11.110501
Enhanced resolution optoacoustic microscopy using a picosecond high repetition rate Q-switched microchip laser
Abstract
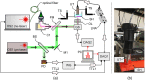
Conventional optoacoustic microscopy (OAM) instruments have at their core a nanosecond pulse duration laser. If lasers with a shorter pulse duration are used, broader, higher frequency ultrasound waves are expected to be generated and as a result, the axial resolution of the instrument is improved. Here, we exploit the advantage offered by a picosecond duration pulse laser to enhance the axial resolution of an OAM instrument. In comparison to an instrument equipped with a 2-ns pulse duration laser, an improvement in the axial resolution of 50% is experimentally demonstrated by using excitation pulses of only 85 ps. To illustrate the capability of the instrument to generate high-quality optoacoustic images, en-face, in-vivo images of the brain of Xenopus laevis tadpole are presented with a lateral resolution of throughout the entire axial imaging range.
Keywords: Q-switched lasers; axial resolution enhancement; optoacoustic.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Treatment of pigmentary disorders in patients with skin of color with a novel 755 nm picosecond, Q-switched ruby, and Q-switched Nd:YAG nanosecond lasers: A retrospective photographic review.Lasers Surg Med. 2016 Feb;48(2):181-7. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22454. Lasers Surg Med. 2016. PMID: 26922302
-
High current short pulse driver using a high power diode laser for optoacoustic biomedical imaging techniques.Opt Express. 2022 Dec 5;30(25):44954-44966. doi: 10.1364/OE.476159. Opt Express. 2022. PMID: 36522908
-
Ablation of porcine ligamentum flavum with Ho:YAG, q-switched Ho:YAG, and quadrupled Nd:YAG lasers.Lasers Surg Med. 2015 Dec;47(10):839-51. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22424. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Lasers Surg Med. 2015. PMID: 26415136 Free PMC article.
-
Towards affordable biomedical imaging: Recent advances in low-cost, high-resolution optoacoustic microscopy.J Microsc. 2025 Apr;298(1):3-9. doi: 10.1111/jmi.13378. Epub 2024 Dec 10. J Microsc. 2025. PMID: 39655863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Picosecond Laser Treatment for Tattoos and Benign Cutaneous Pigmented Lesions (Secondary publication).Laser Ther. 2017 Dec 31;26(4):274-281. doi: 10.5978/islsm.17-RE-02. Laser Ther. 2017. PMID: 29434427 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Photoacoustic imaging plus X: a review.J Biomed Opt. 2024 Jan;29(Suppl 1):S11513. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.29.S1.S11513. Epub 2023 Dec 28. J Biomed Opt. 2024. PMID: 38156064 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dasa M. K., et al. , “Multispectral photoacoustic sensing for accurate glucose monitoring using a supercontinuum laser,” Opt. Soc. Am. J. B: Opt. Phys. 36, A61–A65 (2019).10.1364/JOSAB.36.000A61 - DOI
-
- Irisawa K., et al. , “Influence of laser pulse width to the photoacoustic temporal waveform and the image resolution with a solid-state excitation laser,” Proc. SPIE 8223, 79 (2012).PSISDG10.1117/12.907714 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

