Assessing production variability in empty and filled adeno-associated viruses by single molecule mass analyses
- PMID: 36458114
- PMCID: PMC9706604
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtm.2022.11.003
Assessing production variability in empty and filled adeno-associated viruses by single molecule mass analyses
Abstract
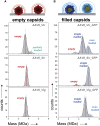
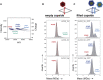
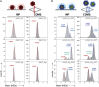
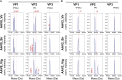
Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) are useful vehicles for gene therapy because of their stability, low immunogenicity. and non-pathogenicity. However, disparity in AAV sample preparations (e.g., in capsid composition, DNA packaging, and impurities) gives rise to product heterogeneity, with possibly undesired effects on gene delivery. Ideally, AAV production should be with full control of AAV structure and genetic payload. Therefore, robust, efficient, and low material consuming methods are essential to characterize AAVs. Here, we use two emerging single-molecule techniques, mass photometry and Orbitrap-based charge-detection mass spectrometry, and show how they may efficiently and accurately characterize AAVs. We were able to resolve heterogeneous pools of particles, evaluating AAVs from two different serotypes (AAV8 and AAV2), produced by three independent production platforms, either lacking a genome or packed with a transgene. Together our data confirm that the different AAV production methods result in rather different and diverse AAV particle distributions. Especially for the packed AAVs, frequently additional subspecies were observed, next to the expected packed genome, mostly resulting from under- or overpackaging of genome material and/or residual empty particles. This work further establishes that both these single-particle techniques may become valuable tools in characterizing AAVs before they are used in gene therapy.
Keywords: AAV biomanufacturing; AAV2; AAV8; Adeno-associated virus; charge-detection mass spectrometry; empty-filled ratio; gene-delivery vector; mass photometry; native mass spectrometry; single molecule mass analyses.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.R., M.N., and M.T. are employees of Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Penzberg, Germany, a company with interest in using AAV vectors for gene-delivery purposes.
Figures

References
-
- Sha S., Maloney A.J., Katsikis G., Nguyen T.N.T., Neufeld C., Wolfrum J., Barone P.W., Springs S.L., Manalis S.R., Sinskey A.J., et al. Cellular pathways of recombinant adeno-associated virus production for gene therapy. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021;49:107764. - PubMed
-
- Li C., Samulski R.J. Engineering adeno-associated virus vectors for gene therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020;21:255–272. - PubMed
-
- Wu Z., Asokan A., Samulski R.J. Adeno-associated virus serotypes: vector toolkit for human gene therapy. Mol. Ther. 2006;14:316–327. - PubMed
-
- Girod A., Wobus C.E., Zádori Z., Ried M., Leike K., Tijssen P., Kleinschmidt J.A., Hallek M. The VP1 capsid protein of adeno-associated virus type 2 is carrying a phospholipase A2 domain required for virus infectivity. J. Gen. Virol. 2002;83:973–978. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

