Liquid biomarkers of macrophage dysregulation and circulating spike protein illustrate the biological heterogeneity in patients with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19
- PMID: 36458566
- PMCID: PMC9878213
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.28364
Liquid biomarkers of macrophage dysregulation and circulating spike protein illustrate the biological heterogeneity in patients with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19
Abstract
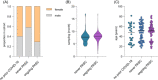
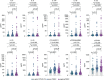
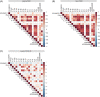
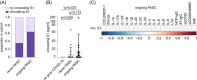
Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) are long-term consequences of SARS-CoV-2 infection that can substantially impair the quality of life. Underlying mechanisms ranging from persistent viruses to innate and adaptive immune dysregulation have been discussed. Here, we profiled the plasma of 181 individuals from the cohort study for digital health research in Germany (DigiHero), including individuals after mild to moderate COVID-19 with or without PASC and uninfected controls. We focused on soluble factors related to monocyte/macrophage biology and on circulating SARS-CoV-2 spike (S1) protein as a potential biomarker for persistent viral reservoirs. At a median time of 8 months after infection, we found pronounced dysregulation in almost all tested soluble factors, including both pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic cytokines. These immunological perturbations were remarkably independent of ongoing PASC symptoms per se, but further correlation and regression analyses suggested PASC-specific patterns involving CCL2/MCP-1 and IL-8 that either correlated with sCD162, sCD206/MMR, IFN-α2, IL-17A and IL-33, or IL-18 and IL-23. None of the analyzed factors correlated with the detectability or levels of circulating S1, indicating that this represents an independent subset of patients with PASC. These data confirm prior evidence of immune dysregulation and persistence of viral protein in PASC and illustrate its biological heterogeneity that still awaits correlation with clinically defined PASC subtypes.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS coronavirus; cytokine/chemokine; long COVID; macrophage; monocyte.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Medical Virology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

