Human Monoclonal IgE Antibodies-a Major Milestone in Allergy
- PMID: 36459330
- PMCID: PMC9831959
- DOI: 10.1007/s11882-022-01055-w
Human Monoclonal IgE Antibodies-a Major Milestone in Allergy
Abstract
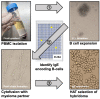
Purpose of review: Bound to its high affinity receptor on mast cells and basophils, the IgE antibody molecule plays an integral role in the allergic reaction. Through interactions with the allergen, it provides the sensitivity and specificity parameters for cell activation and mediator release that produce allergic symptoms. Advancements in human hybridoma technologies allow for the generation and molecular definition of naturally occurring allergen-specific human IgE monoclonal antibodies.
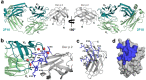
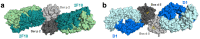
Recent findings: A high-resolution structure of dust mite allergen Der p 2 in complex with Fab of the human IgE mAb 2F10 was recently determined using X-ray crystallography. The structure reveals the fine molecular details of IgE 2F10 binding its 750 Å2 conformational epitope on Der p 2. This review provides an overview of this major milestone in allergy, the first atomic resolution structure of an authentic human IgE epitope. The molecular insights that IgE epitopes provide will allow for structure-based design approaches to the development of novel diagnostics, antibody therapeutics, and immunotherapies.
Keywords: Allergens; Allergy; Conformational epitope; Diagnosis; Human IgE monoclonal antibody; X-ray crystallography.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Scott A Smith reports grants from NIAID R21AI123307, and NIAID R01AI155668, during the conduct of the study; In addition, Dr. Smith has a patent 10,908,168 with royalties paid, a pending patents 63/159,764 and 63/125,099 with royalties paid. Maksymilian Chruszcz declares no conflict of interest. Martin D. Chapman reports grants from NIH—NIAID, during the conduct of the study; and License agreement with Vanderbilt University Medical Center for commercialization of human IgE monoclonal antibodies for research and diagnostic purposes. The hIgE mAb covered by this agreement are available from InBio (
Figures
References
-
- Heeringa JJ, Rijvers L, Arends NJ, Driessen GJ, Pasmans SG, van Dongen JJM, de Jongste JC, van Zelm MC. IgE-expressing memory B cells and plasmablasts are increased in blood of children with asthma, food allergy, and atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 2018;73(6):1331–1336. doi: 10.1111/all.13421. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

