Angiogenic adipokine C1q-TNF-related protein 9 ameliorates myocardial infarction via histone deacetylase 7-mediated MEF2 activation
- PMID: 36459558
- PMCID: PMC10936044
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abq0898
Angiogenic adipokine C1q-TNF-related protein 9 ameliorates myocardial infarction via histone deacetylase 7-mediated MEF2 activation
Abstract
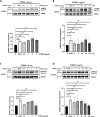
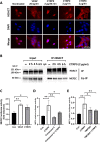
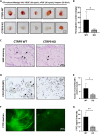
C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein 9 (CTRP9) is an adipokine and has high potential as a therapeutic target. However, the role of CTRP9 in cardiovascular disease pathogenesis remains unclear. We found CTRP9 to induce HDAC7 and p38 MAPK phosphorylation via tight regulation of AMPK in vascular endothelial cells, leading to angiogenesis through increased MEF2 activity. The expression of CTRP9 and atheroprotective MEF2 was decreased in plaque tissue of atherosclerotic patients and the ventricle of post-infarction mice. CTRP9 treatment inhibited the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in ApoE KO and CTRP9 KO mice. In addition, CTRP9 induced significant ischemic injury prevention in the post-MI mice. Clinically, serum CTRP9 levels were reduced in patients with MI compared with healthy controls. In summary, CTRP9 induces a vasoprotective response via the AMPK/HDAC7/p38 MAPK pathway in vascular endothelial cells, whereas its absence can contribute to atherosclerosis and MI. Hence, CTRP9 may represent a valuable therapeutic target and biomarker in cardiovascular diseases.
Figures






Similar articles
-
C1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Protein 9 Protects against Acute Myocardial Injury through an Adiponectin Receptor I-AMPK-Dependent Mechanism.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Jun;35(12):2173-85. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01518-14. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25870106 Free PMC article.
-
C1q/TNF-related protein-9 attenuates atherosclerosis through AMPK-NLRP3 inflammasome singling pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Dec;77:105934. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105934. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31727560
-
C1q/TNF-related protein-9 is elevated in hypertension and associated with the occurrence of hypertension-related atherogenesis.Cell Biol Int. 2021 May;45(5):989-1000. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11542. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Cell Biol Int. 2021. PMID: 33377578
-
C1q/TNF-related protein 9: A novel therapeutic target in ischemic stroke?J Neurosci Res. 2019 Feb;97(2):128-136. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24353. Epub 2018 Oct 31. J Neurosci Res. 2019. PMID: 30378715 Review.
-
C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein 9 in atherosclerosis: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic potential.Atherosclerosis. 2018 Sep;276:109-116. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.07.022. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Atherosclerosis. 2018. PMID: 30056359 Review.
Cited by
-
Multifaced roles of adipokines in endothelial cell function.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 4;15:1490143. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1490143. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39558976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-terminal domain of CTRP9 promotes cardiac fibroblast activation in myocardial infarction via Rap1/Mek/Erk pathway.J Transl Med. 2025 Mar 10;23(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06274-z. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40065407 Free PMC article.
-
Knockout of C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein-9 aggravates cardiac fibrosis in diabetic mice by regulating YAP-mediated autophagy.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 8;15:1407883. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1407883. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39040468 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the roles of CTRP family in cardiac remodeling.J Mol Med (Berl). 2025 Aug;103(8):935-950. doi: 10.1007/s00109-025-02565-6. Epub 2025 Jun 27. J Mol Med (Berl). 2025. PMID: 40579606 Review.
-
Loss of CTRP10 results in female obesity with preserved metabolic health.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 31:2023.11.01.565163. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.01.565163. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Elife. 2025 Mar 24;13:RP93373. doi: 10.7554/eLife.93373. PMID: 37961647 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- GBD 2015 Risk Factors Collaborators , Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990-2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388, 1659–1724 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ghaben A. L., Scherer P. E., Adipogenesis and metabolic health. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 242–258 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Ohashi K., Shibata R., Murohara T., Ouchi N., Role of anti-inflammatory adipokines in obesity-related diseases. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 25, 348–355 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

