Angiogenic adipokine C1q-TNF-related protein 9 ameliorates myocardial infarction via histone deacetylase 7-mediated MEF2 activation
- PMID: 36459558
- PMCID: PMC10936044
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abq0898
Angiogenic adipokine C1q-TNF-related protein 9 ameliorates myocardial infarction via histone deacetylase 7-mediated MEF2 activation
Abstract
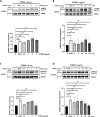
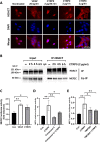
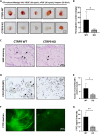
C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein 9 (CTRP9) is an adipokine and has high potential as a therapeutic target. However, the role of CTRP9 in cardiovascular disease pathogenesis remains unclear. We found CTRP9 to induce HDAC7 and p38 MAPK phosphorylation via tight regulation of AMPK in vascular endothelial cells, leading to angiogenesis through increased MEF2 activity. The expression of CTRP9 and atheroprotective MEF2 was decreased in plaque tissue of atherosclerotic patients and the ventricle of post-infarction mice. CTRP9 treatment inhibited the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in ApoE KO and CTRP9 KO mice. In addition, CTRP9 induced significant ischemic injury prevention in the post-MI mice. Clinically, serum CTRP9 levels were reduced in patients with MI compared with healthy controls. In summary, CTRP9 induces a vasoprotective response via the AMPK/HDAC7/p38 MAPK pathway in vascular endothelial cells, whereas its absence can contribute to atherosclerosis and MI. Hence, CTRP9 may represent a valuable therapeutic target and biomarker in cardiovascular diseases.
Figures






References
-
- GBD 2015 Risk Factors Collaborators , Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990-2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388, 1659–1724 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ghaben A. L., Scherer P. E., Adipogenesis and metabolic health. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 242–258 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Ohashi K., Shibata R., Murohara T., Ouchi N., Role of anti-inflammatory adipokines in obesity-related diseases. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 25, 348–355 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

