TRPC channels blockade abolishes endotoxemic cardiac dysfunction by hampering intracellular inflammation and Ca2+ leakage
- PMID: 36460692
- PMCID: PMC9718841
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-35242-0
TRPC channels blockade abolishes endotoxemic cardiac dysfunction by hampering intracellular inflammation and Ca2+ leakage
Abstract
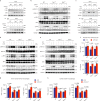
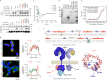
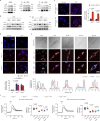
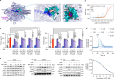
Intracellular Ca2+ dysregulation is a key marker in septic cardiac dysfunction; however, regulation of the classic Ca2+ regulatory modules cannot successfully abolish this symptom. Here we show that the knockout of transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) channel isoforms TRPC1 and TRPC6 can ameliorate LPS-challenged heart failure and prolong survival in mice. The LPS-triggered Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum both in cardiomyocytes and macrophages is significantly inhibited by Trpc1 or Trpc6 knockout. Meanwhile, TRPC's molecular partner - calmodulin - is uncoupled during Trpc1 or Trpc6 deficiency and binds to TLR4's Pococurante site and atypical isoleucine-glutamine-like motif to block the inflammation cascade. Blocking the C-terminal CaM/IP3R binding domain in TRPC with chemical inhibitor could obstruct the Ca2+ leak and TLR4-mediated inflammation burst, demonstrating a cardioprotective effect in endotoxemia and polymicrobial sepsis. Our findings provide insight into the pathogenesis of endotoxemic cardiac dysfunction and suggest a novel approach for its treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
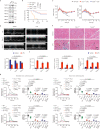
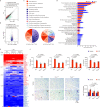
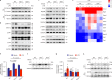
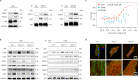
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

