Emergency vaccination of cattle against lumpy skin disease: Evaluation of safety, efficacy, and potency of MEVAC® LSD vaccine containing Neethling strain
- PMID: 36460903
- PMCID: PMC9734455
- DOI: 10.1007/s11259-022-10037-2
Emergency vaccination of cattle against lumpy skin disease: Evaluation of safety, efficacy, and potency of MEVAC® LSD vaccine containing Neethling strain
Abstract
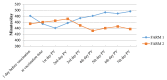
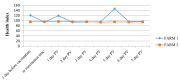
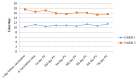
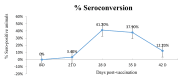
Lumpy skin disease (LSD) is an emerging disease of cattle causing significantly high economic losses. Control of LSD depends on the use of homologous attenuated LSD virus strains isolated originally from South Africa (the Neethling strain). The virus belongs to the genus Capripoxvirus, which includes sheep pox virus and goat pox virus. The present study was conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a new live attenuated LSD vaccine produced by Middle East for Vaccines (MEVAC®) based on the Neethling strain. Tests were performed both in Egypt and Vietnam. Safety was evaluated by inoculation of five cattle with 10 times the recommended dose and observation of the animals for 14 days. Immunogenicity was tested at different periods post-vaccination (PV) in animals receiving the recommended doses of the vaccine using ELISA and virus neutralization test. Five cows were used to determine the protection index (PI) and non-vaccinated control cattle were included. Three calves were challenged by intradermal inoculation of the wild virus (5 × 105 TCID50) 28 days PV. Field or mass vaccination experiments were conducted in Vietnam during national campaigns in the summer of 2021 with 4301 vaccinated animals closely monitored after vaccination. In the field, around 2% (80/4301) of the animals showed hyper-reactivity, and 0.6% (24/4301) showed small skin swellings that disappeared within few hours PV. Abortion was recorded in three animals (0.3% 3/867). Challenged animals were resistant to clinical disease and PI value was 3.5 log10. Meanwhile, antibody levels determined by the ELISA were inconsistent among animals and laboratories during the study period. Overall, the findings point to a new safe and effective LSD vaccine.
Keywords: Lumpy skin disease; Neethling strain; Post-vaccination reaction; Seroconversion; Vaccine; Vaccine evaluation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Magdy M. El-Sayed is a member of MEVAC’s board of directors. Momtaz Wasfy and Randa Y. Thabet are employees in Middle East for Vaccines (ME VAC®). Hui Sian Yong is an employer at Kemin Biologisc®; MEVAC® now is a part of Kemin®. However, this association has no effect on the study’s design, data analysis, results’ interpretation, or publication decision.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the safety, immunogenicity and efficacy of three capripoxvirus vaccine strains against lumpy skin disease virus.Vaccine. 2015 Jun 22;33(28):3256-61. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.01.035. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 26056063
-
Comparison of the efficacy of Neethling lumpy skin disease virus and x10RM65 sheep-pox live attenuated vaccines for the prevention of lumpy skin disease - The results of a randomized controlled field study.Vaccine. 2015 Sep 11;33(38):4837-42. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.07.071. Epub 2015 Aug 1. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 26238726 Clinical Trial.
-
Goatpox virus (G20-LKV) vaccine strain elicits a protective response in cattle against lumpy skin disease at challenge with lumpy skin disease virulent field strain in a comparative study.Vet Microbiol. 2020 Jun;245:108695. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2020.108695. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Vet Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32456811
-
Vaccines for lumpy skin disease, sheep pox and goat pox.Dev Biol (Basel). 2003;114:161-7. Dev Biol (Basel). 2003. PMID: 14677686 Review.
-
Progress in diagnostic methods and vaccines for lumpy skin disease virus: a path towards understanding the disease.Vet Res Commun. 2025 Mar 8;49(3):134. doi: 10.1007/s11259-025-10667-2. Vet Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40056298 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of mass vaccination policy and control measures on lumpy skin disease cases in Thailand: insights from a Bayesian structural time series analysis.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Jan 5;10:1301546. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1301546. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38249552 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Research on Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD) in Psychiatry and Neuroscience.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Mar 29;18(4):499. doi: 10.3390/ph18040499. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Inhibitors of Lumpy Skin Disease's Viral Protein (DNA Polymerase): A Combination of Bioinformatics Approaches.Animals (Basel). 2024 Apr 24;14(9):1283. doi: 10.3390/ani14091283. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38731287 Free PMC article.
-
The Current Epizootiological Situation of Three Major Viral Infections Affecting Cattle in Egypt.Viruses. 2024 Sep 28;16(10):1536. doi: 10.3390/v16101536. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39459870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of antibody titer and associated risk factors of goat pox vaccine against lumpy skin disease in crossbred buffaloes.Vet Res Commun. 2025 Feb 14;49(2):104. doi: 10.1007/s11259-025-10673-4. Vet Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 39951183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agianniotaki EI, Chaintoutis SC, Haegeman A, Tasioudi KE, De Leeuw I, Katsoulos PD, Sachpatzidis A, De Clercq K, Alexandropoulos T, Polizopoulou ZS, Chondrokouki ED, Dovas CI. Development and validation of a TaqMan probe-based real-time PCR method for the differentiation of wild type lumpy skin disease virus from vaccine virus strains. J Virol Methods. 2017;249:48–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2017.08.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Agianniotaki EI, Babiuk S, Katsoulos P-D, Chaintoutis Serafeim C, Praxitelous A, Quizon K, Boscos C, Polizopoulou ZS, Chondrokouki ED, Dovas CI. Colostrum transfer of neutralizing antibodies against lumpy skin disease virus from vaccinated cows to their calves. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2018;65(6):2043–2048. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12983. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

