Early prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy combining DCE-MRI and apparent diffusion coefficient values in breast Cancer
- PMID: 36460972
- PMCID: PMC9716688
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-10315-x
Early prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy combining DCE-MRI and apparent diffusion coefficient values in breast Cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Improving the early prediction of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) efficacy in breast cancer can lead to an improved prediction of the final prognosis of patients, which would be useful for promoting individualized treatment. This study aimed to explore the value of the combination of dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE)-MRI parameters and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values in the early prediction of pathological complete response (pCR) to NAC for breast cancer.
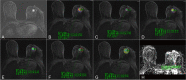
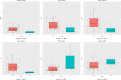
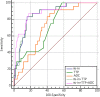
Methods: A total of 119 (range, 28-69 years) patients with biopsy-proven breast cancer who received two cycles of NAC before breast surgery were retrospectively enrolled from our hospital database. Patients were divided into pCR and non pCR groups according to their pathological responses; a total of 24 patients achieved pCR, while 95 did not. The quantitative (Ktrans; Kep; Ve; IAUC) and semiquantitative parameters (W-in; W-out; TTP) of DCE-MRI that were significantly different between groups were combined with ADC values to explore their value in the early prediction of pCR to NAC for breast cancer. The independent T test was performed to compare the differences in DCE-MRI parameters and ADC values between the two groups. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted, and the area under the ROC curve (AUC), sensitivity and specificity were calculated to evaluate the performance of the prediction.
Results: The Ktrans, Kep, IAUC, ADC, W-in and TTP values were significantly different between the pCR and non pCR groups after NAC. The AUC (0.845) and specificity (95.79%) of the combined Ktrans, Kep, IAUC and ADC values were both higher than those of the individual parameters. The combination of W-in, TTP and ADC values had the highest AUC value (0.886) in predicting pCR, with a sensitivity and specificity of 87.5% and 82.11%, respectively.
Conclusions: The results suggested that the combination of ADC values and quantitative and semiquantitative DCE-MRI parameters, especially the combination of W-in, TTP, and ADC values, may improve the early prediction of pCR in breast cancer.
Keywords: DCE-MRI; Neoadjuvant chemotherapy; apparent diffusion coefficient values; breast cancer; treatment response.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for predicting pathological response after the first cycle of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer.Invest Radiol. 2015 Apr;50(4):195-204. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000100. Invest Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25360603 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Machine Learning With Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Breast for Early Prediction of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Survival Outcomes in Breast Cancer Patients.Invest Radiol. 2019 Feb;54(2):110-117. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000518. Invest Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30358693 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic contrast-enhanced and diffusion-weighted MR imaging in early prediction of pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced gastric cancer.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2022 Oct;47(10):3394-3405. doi: 10.1007/s00261-022-03623-0. Epub 2022 Aug 2. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2022. PMID: 35916943
-
Meta-Analysis of Quantitative Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI for the Assessment of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer.Am Surg. 2019 Jun 1;85(6):645-653. Am Surg. 2019. PMID: 31267907 Review.
-
Meta-Analysis of MRI in Predicting Early Response to Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy in Esophageal Cancer.Acad Radiol. 2025 Feb;32(2):798-812. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2024.08.055. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Acad Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39266443
Cited by
-
Exploring Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy, Predictive Models, Radiomic, and Pathological Markers in Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 4;15(21):5288. doi: 10.3390/cancers15215288. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accuracy of MRI Versus PET/CT in the Prediction of Treatment Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer.Cureus. 2024 Aug 4;16(8):e66114. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66114. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39108769 Free PMC article.
-
The comparison between young and old patients and the prognostic roles of magnetic resonance imaging-related parameter characteristics in young patients-a retrospective cohort study.Gland Surg. 2023 Apr 28;12(4):465-473. doi: 10.21037/gs-23-84. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Gland Surg. 2023. PMID: 37200928 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a point-based scoring system for predicting axillary lymph node metastasis and disease outcome in breast cancer using clinicopathological and multiparametric MRI features.Cancer Imaging. 2023 Jun 1;23(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s40644-023-00564-9. Cancer Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37264446 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for differentiating HER2-zero, HER2-low, and HER2-positive breast cancers in patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Feb 25;30(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02188-6. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40001120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ryu JM, Lee SK, Kim JY, Yu J, Kim SW, Lee JE, Han SH, Jung YS, Nam SJ. Predictive Factors for Nonsentinel Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients With Positive Sentinel Lymph Nodes After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Nomogram for Predicting Nonsentinel Lymph Node Metastasis. Clinical breast cancer. 2017;17(7):550–558. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2017.03.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Chen X, Yang J, Li Y, Fan W, Yang Z. Combining Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Maps for a Radiomics Nomogram to Predict Pathological Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2020;44(2):275–283. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000000978. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dong JM, Wang HX, Zhong XF, Xu K, Bian J, Feng Y, Chen L, Zhang L, Wang X, Ma DJ, et al. Changes in background parenchymal enhancement in HER2-positive breast cancer before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: Association with pathologic complete response. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97(43):e12965. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012965. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

