The effect of non-oncology drugs on clinical and genomic risk in early luminal breast cancer
- PMID: 36462463
- PMCID: PMC9808449
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100648
The effect of non-oncology drugs on clinical and genomic risk in early luminal breast cancer
Abstract
Background: An effect of non-oncology medications on cancer outcome has been proposed. In this study, we aimed to systematically examine the impact of commonly prescribed non-oncology drugs on clinical risk and on the genomic risk [based on the Oncotype DX recurrence score (RS)] in early breast cancer (BC).
Experimental design: We collected data on clinical risk (stage and grade), genomic risk (Oncotype DX RS), and on non-oncology medications administered to 1423 patients with estrogen receptor-positive human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative BC during the month of their surgery. The influence of various medications on clinical and genomic risks was evaluated by statistical analysis.
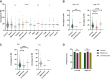
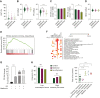
Results: Out of the multiple drugs we examined, levothyroxine was significantly associated with a high Oncotype DX RS (mean 24.78; P < 0.0001) and metformin with a low Oncotype DX RS (mean 14.87; P < 0.01) compared with patients not receiving other non-oncology drugs (mean 18.7). By contrast, there were no differences in the clinical risk between patients receiving metformin, levothyroxine, or no other non-oncology drugs. Notably, there was no association between the consumption of levothyroxine and metformin and proliferation marker (Ki67) levels, but both drugs were significantly associated with progesterone-related features, suggesting that they influence genomic risk through estrogen-dependent signaling.
Conclusions: The results of this study indicate a significant impact of metformin and levothyroxine on clinical decisions in luminal BC, with potential impact on the clinical course of these patients.
Keywords: Oncotype DX; breast cancer; clinical risk; estrogen receptor; genomic risk; levothyroxine; metformin.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Cardoso F., van’t Veer L.J., Bogaerts J., et al. 70-gene signature as an aid to treatment decisions in early-stage breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:717–729. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Angulo A.M., Barlow W.E., Gralow J., et al. SWOG S1007: a phase III, randomized clinical trial of standard adjuvant endocrine therapy with or without chemotherapy in patients with one to three positive nodes, hormone receptor (HR)-positive, and HER2-negative breast cancer with recurrence score (RS) J Clin Oncol. 2011;29 doi: 10.1200/jco.2011.29.15_suppl.tps104. - DOI
-
- Dowsett M., Cuzick J., Wale C., et al. Prediction of risk of distant recurrence using the 21-gene recurrence score in node-negative and node-positive postmenopausal patients with breast cancer treated with anastrozole or tamoxifen: a TransATAC study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1829–1834. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

