Medical Nutrition Therapy Interventions Provided by Dietitians for Adult Overweight and Obesity Management: An Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Evidence-Based Practice Guideline
- PMID: 36462613
- PMCID: PMC12646719
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jand.2022.11.014
Medical Nutrition Therapy Interventions Provided by Dietitians for Adult Overweight and Obesity Management: An Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Evidence-Based Practice Guideline
Abstract
Overweight and obesity affect most adults living in the United States and are causally linked to several adverse health outcomes. Registered dietitian nutritionists or international equivalents (dietitians) collaborate with each client and other health care professionals to meet client-centered goals, informed by the best available evidence, and translated through a lens of clinical expertise and client circumstances and preferences. Since the last iteration of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics guideline on adult weight management in 2014, considerable research has been conducted and circumstances confronting dietitians have evolved. Thus, updated guidance is needed. The objective of this evidence-based practice guideline is to provide recommendations for dietitians who deliver medical nutrition therapy behavioral interventions for adults (18 years and older) with overweight and obesity to improve cardiometabolic outcomes, quality of life, and weight outcomes, when appropriate for and desired by the client. Recommendations in this guideline highlight the importance of considering complex contributors to overweight and obesity and individualizing interventions to client-centered goals based on specific needs and preferences and shared decision making. The described recommendations have the potential to increase access to care and decrease costs through utilization of telehealth and group counseling as effective delivery methods, and to address other barriers to overweight and obesity management interventions. It is essential for dietitians to collaborate with clients and interprofessional health care teams to provide high-quality medical nutrition therapy interventions using the nutrition care process to promote attainment of client-centered outcomes for adults with overweight or obesity.
Copyright © 2023 Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
STATEMENT OF POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Conflict of interest was assessed prior to joining the expert panel, during each expert panel meeting, and following the guideline. H. A. Raynor is the principal investigator on National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant on child weight management (5R01DK121360) and co-editor of the Academy’s
Figures



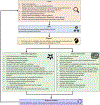
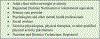


References
-
- Adult obesity facts. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Published 2021. Accessed June 30, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/adult.html
-
- Defining adult overweight & obesity. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Obesity, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. Published 2021. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/basics/adult-defining.html
-
- Yu HJ, Ho M, Liu X, Yang J, Chau PH, Fong DYT. Association of weight status and the risks of diabetes in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Int J Obes (Lond). 2022;46(6):1101–1113. - PubMed
-
- Jayedi A, Rashidy-Pour A, Khorshidi M, Shab-Bidar S. Body mass index, abdominal adiposity, weight gain and risk of developing hypertension: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of more than 2.3 million participants. Obes Rev 2018;19(5):654–667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

