Exogenous laminin exhibits a unique vascular pattern in the brain via binding to dystroglycan and integrins
- PMID: 36463265
- PMCID: PMC9719645
- DOI: 10.1186/s12987-022-00396-y
Exogenous laminin exhibits a unique vascular pattern in the brain via binding to dystroglycan and integrins
Abstract
Background: Unlike other proteins that exhibit a diffusion pattern after intracerebral injection, laminin displays a vascular pattern. It remains unclear if this unique vascular pattern is caused by laminin-receptor interaction or laminin self-assembly.
Methods: We compared the distribution of various wild-type laminin isoforms in the brain after intracerebral injection. To determine what causes the unique vascular pattern of laminin in the brain, laminin mutants with impaired receptor-binding and/or self-assembly activities and function-blocking antibodies to laminin receptors were used. In addition, the dynamics of laminin distribution and elimination were examined at multiple time points after intracerebral injection.
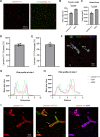
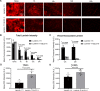
Results: We found that β2-containing laminins had higher affinity for the vessels compared to β1-containing laminins. In addition, laminin mutants lacking receptor-binding domains but not that lacking self-assembly capability showed substantially reduced vascular pattern. Consistent with this finding, dystroglycan (DAG1) function-blocking antibody significantly reduced the vascular pattern of wild-type laminin-111. Although failed to affect the vascular pattern when used alone, integrin-β1 function-blocking antibody further decreased the vascular pattern when combined with DAG1 antibody. EDTA, which impaired laminini-DAG1 interaction by chelating Ca2+, also attenuated the vascular pattern. Immunohistochemistry revealed that laminins were predominantly located in the perivascular space in capillaries and venules/veins but not arterioles/arteries. The time-course study showed that laminin mutants with impaired receptor-engaging activity were more efficiently eliminated from the brain compared to their wild-type counterparts. Concordantly, significantly higher levels of mutant laminins were detected in the cerebral-spinal fluid (CSF).
Conclusions: These findings suggest that intracerebrally injected laminins are enriched in the perivascular space in a receptor (DAG1/integrin)-dependent rather than self-assembly-dependent manner and eliminated from the brain mainly via the perivascular clearance system.
Keywords: Dystroglycan; Integrins; Laminin; Perivascular space; Vascular pattern.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Laminin β2 Chain Regulates Retinal Progenitor Cell Mitotic Spindle Orientation via Dystroglycan.J Neurosci. 2018 Jun 27;38(26):5996-6010. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0551-18.2018. Epub 2018 May 31. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29853630 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing roles of integrin alpha6Abeta1 and dystroglycan in laminin-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 May;14(5):2088-103. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-01-0852. Epub 2003 Feb 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12802077 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal region of laminin beta chains modulates the integrin binding affinities of laminins.J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 20;284(12):7820-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809332200. Epub 2009 Jan 15. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19147489 Free PMC article.
-
Non-integrin laminin receptors in epithelia.Tissue Cell. 2019 Feb;56:71-78. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2018.12.005. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Tissue Cell. 2019. PMID: 30736907 Review.
-
Laminins: structure and genetic regulation.Microsc Res Tech. 2000 Nov 1;51(3):214-27. doi: 10.1002/1097-0029(20001101)51:3<214::AID-JEMT2>3.0.CO;2-J. Microsc Res Tech. 2000. PMID: 11054872 Review.
Cited by
-
Activated alpha 9 integrin expression enables sensory pathway reconstruction after spinal cord injury.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025 May 2;13(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s40478-025-01995-0. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025. PMID: 40317093 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the mechanisms of the extracellular matrix and its therapeutic potential in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 9;14(1):20977. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72020-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39251678 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

