The multivalency of the glucocorticoid receptor ligand-binding domain explains its manifold physiological activities
- PMID: 36464162
- PMCID: PMC9825158
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkac1119
The multivalency of the glucocorticoid receptor ligand-binding domain explains its manifold physiological activities
Abstract
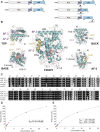
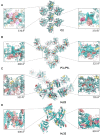
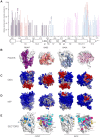
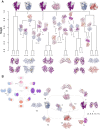
The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is a ubiquitously expressed transcription factor that controls metabolic and homeostatic processes essential for life. Although numerous crystal structures of the GR ligand-binding domain (GR-LBD) have been reported, the functional oligomeric state of the full-length receptor, which is essential for its transcriptional activity, remains disputed. Here we present five new crystal structures of agonist-bound GR-LBD, along with a thorough analysis of previous structural work. We identify four distinct homodimerization interfaces on the GR-LBD surface, which can associate into 20 topologically different homodimers. Biologically relevant homodimers were identified by studying a battery of GR point mutants including crosslinking assays in solution, quantitative fluorescence microscopy in living cells, and transcriptomic analyses. Our results highlight the relevance of non-canonical dimerization modes for GR, especially of contacts made by loop L1-3 residues such as Tyr545. Our work illustrates the unique flexibility of GR's LBD and suggests different dimeric conformations within cells. In addition, we unveil pathophysiologically relevant quaternary assemblies of the receptor with important implications for glucocorticoid action and drug design.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research 2022.
Figures

Similar articles
-
First High-Resolution Crystal Structures of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Ligand-Binding Domain-Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated γ Coactivator 1-α Complex with Endogenous and Synthetic Glucocorticoids.Mol Pharmacol. 2019 Oct;96(4):408-417. doi: 10.1124/mol.119.116806. Epub 2019 Aug 7. Mol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31391291 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative dimerization interfaces in the glucocorticoid receptor-α ligand binding domain.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018 Aug;1862(8):1810-1825. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.04.022. Epub 2018 May 1. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018. PMID: 29723544
-
Structural Insights into the Ligand Binding Domain of the Glucocorticoid Receptor: A Molecular Dynamics Study.J Chem Inf Model. 2020 Feb 24;60(2):794-804. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00776. Epub 2019 Nov 14. J Chem Inf Model. 2020. PMID: 31689103
-
21-Hydroxy-6,19-epoxyprogesterone: A Promising Therapeutic Agent and a Molecular Tool for Deciphering Glucocorticoid Action.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018 Feb 14;18(5):428-438. doi: 10.2174/1389557516666160118112313. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 26776223 Review.
-
Structure and function of the glucocorticoid receptor ligand binding domain.Vitam Horm. 2004;68:49-91. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(04)68002-2. Vitam Horm. 2004. PMID: 15193451 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription factors form a ternary complex with NIPBL/MAU2 to localize cohesin at enhancers.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 19:2024.12.09.627537. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.09.627537. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 May 10;53(9):gkaf415. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf415. PMID: 39713324 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Glucocorticoid receptor controls atopic dermatitis inflammation via functional interactions with P63 and autocrine signaling in epidermal keratinocytes.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jul 28;15(7):535. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06926-w. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39069531 Free PMC article.
-
Phase-separation: a possible new layer for transcriptional regulation by glucocorticoid receptor.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 14;14:1160238. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1160238. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37124728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Biologist's Guide to the Glucocorticoid Receptor's Structure.Cells. 2023 Jun 15;12(12):1636. doi: 10.3390/cells12121636. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37371105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stereoisomers of an Aryl Pyrazole Glucocorticoid Receptor Agonist Scaffold Elicit Differing Anti-inflammatory Responses.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2022 Aug 22;13(9):1493-1499. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00299. eCollection 2022 Sep 8. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 36105346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Conway-Campbell B.L., Pooley J.R., Hager G.L., Lightman S.L.. Molecular dynamics of ultradian glucocorticoid receptor action. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2011; 348:383–393. - PubMed
-
- Busada J.T., Cidlowski J.A.. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid action during development. Curr. Top Dev. Biol. 2017; 125:147–170. - PubMed
-
- Bledsoe R.K., Montana V.G., Stanley T.B., Delves C.J., Apolito C.J., McKee D.D., Consler T.G., Parks D.J., Stewart E.L., Willson T.M.et al. .. Crystal structure of the glucocorticoid receptor ligand binding domain reveals a novel mode of receptor dimerization and coactivator recognition. Cell. 2002; 110:93–105. - PubMed
-
- Jimenez-Panizo A., Perez P., Rojas A., Fuentes-Prior P., Estebanez-Perpina E.. Non-canonical dimerization of the androgen receptor and other nuclear receptors: implications for human disease. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 2019; 26:R479–R497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

