Enhanced sentiment analysis regarding COVID-19 news from global channels
- PMID: 36465148
- PMCID: PMC9702932
- DOI: 10.1007/s42001-022-00189-1
Enhanced sentiment analysis regarding COVID-19 news from global channels
Abstract
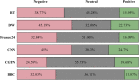
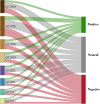
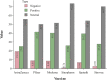
For a healthy society to exist, it is crucial for the media to focus on disease-related issues so that more people are widely aware of them and reduce health risks. Recently, deep neural networks have become a popular tool for textual sentiment analysis, which can provide valuable insights and real-time monitoring and analysis regarding health issues. In this paper, as part of an effort to develop an effective model that can elicit public sentiment on COVID-19 news, we propose a novel approach Cov-Att-BiLSTM for sentiment analysis of COVID-19 news headlines using deep neural networks. We integrate attention mechanisms, embedding techniques, and semantic level data labeling into the prediction process to enhance the accuracy. To evaluate the proposed approach, we compared it to several deep and machine learning classifiers using various metrics of categorization efficiency and prediction quality, and the experimental results demonstrate its superiority with 0.931 testing accuracy. Furthermore, 73,138 pandemic-related tweets posted on six global channels were analyzed by the proposed approach, which accurately reflects global coverage of COVID-19 news and vaccination.
Keywords: COVID-19; Deep learning; News media; Sentiment analysis; Vaccine.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd. 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestOn behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
A hybrid transformer and attention based recurrent neural network for robust and interpretable sentiment analysis of tweets.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 22;14(1):24882. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76079-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39438715 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing News Articles and Tweets About COVID-19 in Brazil: Sentiment Analysis and Topic Modeling Approach.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2021 Feb 10;7(2):e24585. doi: 10.2196/24585. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2021. PMID: 33480853 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine sentiment analysis using BERT + NBSVM and geo-spatial approaches.J Supercomput. 2023 May 7:1-31. doi: 10.1007/s11227-023-05319-8. Online ahead of print. J Supercomput. 2023. PMID: 37359330 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the Utility of Social Media in COVID-19 Vaccination: Unsupervised Learning of 672,133 Twitter Posts.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2021 Nov 3;7(11):e29789. doi: 10.2196/29789. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2021. PMID: 34583316 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Related Sentiment Analysis Using State-of-the-Art Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques.Front Public Health. 2022 Jan 14;9:812735. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.812735. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35096755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abercrombie G, Batista-Navarro R. Sentiment and position-taking analysis of parliamentary debates: a systematic literature review. Journal of Computational Social Science. 2020;3(1):245–270. doi: 10.1007/s42001-019-00060-w. - DOI
-
- Agarwal A, Agarwal B, Harjule P, Agarwal A. Predictive and preventive measures for Covid-19 pandemic. Singapore: Springer; 2021. Mental health analysis of students in major cities of India during COVID-19; pp. 51–67.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
