SIRT6 in Aging, Metabolism, Inflammation and Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 36465178
- PMCID: PMC9662279
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2022.0413
SIRT6 in Aging, Metabolism, Inflammation and Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
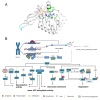
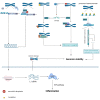
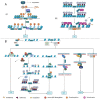
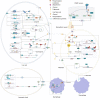
As an important NAD+-dependent enzyme, SIRT6 has received significant attention since its discovery. In view of observations that SIRT6-deficient animals exhibit genomic instability and metabolic disorders and undergo early death, SIRT6 has long been considered a protein of longevity. Recently, growing evidence has demonstrated that SIRT6 functions as a deacetylase, mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase and long fatty deacylase and participates in a variety of cellular signaling pathways from DNA damage repair in the early stage to disease progression. In this review, we elaborate on the specific substrates and molecular mechanisms of SIRT6 in various physiological and pathological processes in detail, emphasizing its links to aging (genomic damage, telomere integrity, DNA repair), metabolism (glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, insulin secretion and lipid synthesis, lipolysis, thermogenesis), inflammation and cardiovascular diseases (atherosclerosis, cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure, ischemia-reperfusion injury). In addition, the most recent advances regarding SIRT6 modulators (agonists and inhibitors) as potential therapeutic agents for SIRT6-mediated diseases are reviewed.
Keywords: SIRT6; ageing; cardiovascular diseases; inflammation; metabolism; molecular network.
copyright: © 2022 Guo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests There is no conflict of interest involved in this review.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Role and Molecular Pathways of SIRT6 in Senescence and Age-related Diseases.Adv Biol (Weinh). 2025 Apr;9(4):e2400469. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202400469. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39913122 Review.
-
SIRT6 in Senescence and Aging-Related Cardiovascular Diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 29;9:641315. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.641315. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33855020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological and catalytic functions of sirtuin 6 as targets for small-molecule modulators.J Biol Chem. 2020 Aug 7;295(32):11021-11041. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.011438. Epub 2020 Jun 9. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32518153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatin and beyond: the multitasking roles for SIRT6.Trends Biochem Sci. 2014 Feb;39(2):72-81. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2013.12.002. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Trends Biochem Sci. 2014. PMID: 24438746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuin 6: a review of biological effects and potential therapeutic properties.Mol Biosyst. 2013 Jul;9(7):1789-806. doi: 10.1039/c3mb00001j. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Mol Biosyst. 2013. PMID: 23592245 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of SIRT6 aggravates p53-mediated ferroptosis in acute lung injury in mice.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 11;9(11):e22272. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22272. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38034611 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial dysfunction: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications.MedComm (2020). 2024 Jul 22;5(8):e651. doi: 10.1002/mco2.651. eCollection 2024 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39040847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Increased Expression of Sirtuin 6 in the Prevention of Premature Aging Pathomechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 2;24(11):9655. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119655. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol suppresses hepatic fatty acid synthesis and increases fatty acid β-oxidation via the microRNA-33/SIRT6 signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2024 Jun 19;28(2):326. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12615. eCollection 2024 Aug. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 38979023 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin 6 Regulates the Activation of the ATP/Purinergic Axis in Endothelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 4;24(7):6759. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076759. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Imai S, Armstrong CM, Kaeberlein M, Guarente L (2000). Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. Nature, 403:795-800. - PubMed
-
- Schutkowski M, Fischer F, Roessler C, Steegborn C (2014). New assays and approaches for discovery and design of Sirtuin modulators. Expert Opin Drug Discov, 9:183-199. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
