ESPL1 is Elevated in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Predicts Prognosis
- PMID: 36465268
- PMCID: PMC9717693
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S381188
ESPL1 is Elevated in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Predicts Prognosis
Abstract
Purpose: The extra spindle pole bodies-like 1 (ESPL1) gene is associated with malignant biological behaviors in several tumors. Nevertheless, the correlation between hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and ESPL1 has not been determined. The present study analyzed the molecular function and prognostic value of ESPL1 in HCC.
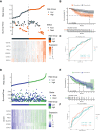
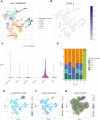
Patients and methods: Samples from 121 HCCs and 119 adjacent normal tissue specimens were subjected to next-generation sequencing. Clinicopathological and genetic data of HCC patients in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) were also collected. ESPL1 expression was assessed in 20 pairs of HCC and normal liver specimens by qRT-PCR and immunohistochemistry (IHC). The prognostic value of ESPL1 expression was determined by Cox univariate and multivariate regression analyses. ESPL1-related co-expressed genes were evaluated by weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA). Processes and pathways involving ESPL1 in HCC were determined by Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses. The prognostic values of hub genes were determined by joint effect survival analysis.
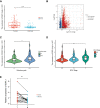
Results: RNA-Seq, RT-qPCR and IHC showed that ESPL1 expression was significantly higher in HCC than in normal liver tissues. Increased ESPL1 expression, greater tumor size and advanced BCLC stage were independently prognostic of poorer overall survival; and increased ESPL1 and advanced BCLC stage were independently prognostic of poorer recurrence-free survival. WGCNA showed that the top 10 co-expressed genes associated with ESPL1 were GTSE1, KIF18B, BUB1B, GINS1, PRC1, KIF23, KIF18A, TOP2A, NEK2 and FANCD2. Enrichment analysis indicated that ESPL1 and its co-expressed genes might be involved in the cell cycle and cell division of HCC. Joint effect survival analysis showed that the mortality rate was approximately 3.37 times higher in HCC patients with high than low expression of ESPL1, GTSE1, BUB1B, PRC1, KIF23, and TOP2A.
Conclusion: ESPL1 might be associated with cell cycle and might be an effective prognostic indicator in patients with HCC.
Keywords: extra spindle pole bodies-like 1; hepatocellular carcinoma; prognosis.
© 2022 Song et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Extra Spindle Pole Bodies-Like 1 Serves as a Prognostic Biomarker and Promotes Lung Adenocarcinoma Metastasis.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 22;12:930647. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.930647. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35814478 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of 40S ribosomal protein S8 as a novel biomarker for alcohol‑associated hepatocellular carcinoma using weighted gene co‑expression network analysis.Oncol Rep. 2020 Aug;44(2):611-627. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7634. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32627011 Free PMC article.
-
Screening Hub Genes as Prognostic Biomarkers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Bioinformatics Analysis.Cell Transplant. 2019 Dec;28(1_suppl):76S-86S. doi: 10.1177/0963689719893950. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Cell Transplant. 2019. PMID: 31822116 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 665 (LINC00665) Gene and the Cell Cycle in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using The Cancer Genome Atlas, the Gene Expression Omnibus, and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction.Med Sci Monit. 2018 May 5;24:2786-2808. doi: 10.12659/MSM.907389. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 29728556 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Core Genes Related to Progression and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Small-Molecule Drug Predication.Front Genet. 2021 Feb 23;12:608017. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.608017. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33708237 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluating serum extra spindle pole bodies-like 1 protein vs p53 antibody for hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis.World J Hepatol. 2025 Jul 27;17(7):108850. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.108850. World J Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40747232 Free PMC article.
-
PAX2 mediated upregulation of ESPL1 contributes to cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer through activating the JAK2/STAT3 pathway.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Sep;397(9):6889-6901. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03061-3. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38573552
-
Novel strategy for activating gene expression through triplex DNA formation targeting epigenetically suppressed genes.RSC Chem Biol. 2024 Jul 31;5(9):884-890. doi: 10.1039/d4cb00134f. eCollection 2024 Aug 28. RSC Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 39211471 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct Transcriptomic and Tumor Microenvironment Profiles in Sinonasal Mucosal Melanoma and Aggressive Cutaneous Melanomas.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 14;16(24):4172. doi: 10.3390/cancers16244172. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766071 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of serum ESPL1 as a biomarker for early diagnosis of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 3;15:1574317. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1574317. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40248196 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

