Association between differential somatic cell count and California Mastitis Test results in Holstein cattle
- PMID: 36465503
- PMCID: PMC9709608
- DOI: 10.3168/jdsc.2022-0249
Association between differential somatic cell count and California Mastitis Test results in Holstein cattle
Abstract
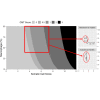
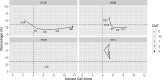
The California Mastitis Test (CMT) has been used to estimate total somatic cell count (SCC) levels in milk; however, milk with similar SCC levels occasionally shows inconsistent CMT results, which limits the use of the CMT. This observational study aimed to investigate how differential cell counts in milk influence the CMT in Holstein cattle through the novel parameters differential somatic cell count (DSCC) and macrophage proportion (MAC). We performed the CMT on d 0, 3, 5, 7, 14, and 21 after identifying mastitis, and simultaneously measured SCC, DSCC, and MAC at the quarter level. We followed 58 mastitis events occurring in 41 cows and obtained 307 quarter-level records after data cleaning. We transformed SCC to somatic cell score (SCS) and MAC to its logarithm to fit the normal distribution and analyzed the data using the cumulative logit mixed model. Results showed that both an increase in SCS (odds ratio: 3.66, 95% confidence interval: 2.89-4.64) and the logarithm of MAC (odds ratio: 4.35, 95% confidence interval: 1.91-9.91) can contribute to a higher CMT score. During the healing process of mastitis, MAC tends to increase as SCC decreases; thus, even samples with low SCC can cause positive CMT reactions. We recommend that practitioners avoid making treatment decisions based on the CMT alone. We also noted that the CMT is sensitive to subclinical mastitis with high MAC, hence it could be considered an alternative to detecting high MAC (chronic) mastitis.
© 2022.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic parameters of differential somatic cell count, milk composition, and cheese-making traits measured and predicted using spectral data in Holstein cows.J Dairy Sci. 2021 Oct;104(10):10934-10949. doi: 10.3168/jds.2021-20395. Epub 2021 Jul 10. J Dairy Sci. 2021. PMID: 34253356
-
Randomized controlled field trial comparing quarter and cow level selective dry cow treatment using the California Mastitis Test.J Dairy Sci. 2021 Aug;104(8):9063-9081. doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-19258. Epub 2021 Apr 30. J Dairy Sci. 2021. PMID: 33934854
-
Bacteriological outcomes following random allocation to quarter-level selection based on California Mastitis Test score or cow-level allocation based on somatic cell count for dry cow therapy.J Dairy Sci. 2022 Mar;105(3):2453-2472. doi: 10.3168/jds.2021-21020. Epub 2022 Jan 25. J Dairy Sci. 2022. PMID: 35086708
-
Novel insights into the associations between immune cell population distribution in mammary glands and milk minerals in Holstein cows.J Dairy Sci. 2024 Jan;107(1):593-606. doi: 10.3168/jds.2023-23729. Epub 2023 Sep 9. J Dairy Sci. 2024. PMID: 37690723
-
Use of somatic cell counts and California mastitis test results from individual quarter milk samples to detect subclinical intramammary infection in dairy cattle from a herd with a high bulk tank somatic cell count.J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2004 Feb 1;224(3):419-23. doi: 10.2460/javma.2004.224.419. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2004. PMID: 14765803
Cited by
-
Subclinical Mastitis in Small-Holder Dairy Herds of Gansu Province, Northwest China: Prevalence, Bacterial Pathogens, Antimicrobial Susceptibility, and Risk Factor Analysis.Microorganisms. 2024 Dec 20;12(12):2643. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12122643. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39770845 Free PMC article.
-
Intramammary Infusion of Micronised Purified Flavonoid Fraction (MPFF) in Mastitis-Diagnosed Dairy Cows Naturally Infected by Staphylococcus spp. in the Late Lactation.Vet Sci. 2023 May 6;10(5):335. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10050335. Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37235418 Free PMC article.
-
The Accurate and Exclusive Quantification of Somatic Cells in Raw Milk with an OPD-Cu2+ System-Based Colorimetric Method.Foods. 2024 Sep 12;13(18):2890. doi: 10.3390/foods13182890. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39335819 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and phenotypic identification of bacterial species isolated from cows with mastitis from three regions of Poland.BMC Vet Res. 2024 May 11;20(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s12917-023-03869-w. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38734661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bobbo T., Penasa M., Cassandro M. Combining total and differential somatic cell count to better assess the association of udder health status with milk yield, composition and coagulation properties in cattle. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2020;19:697–703. doi: 10.1080/1828051X.2020.1784804. - DOI
-
- Christensen R.H.B. Ordinal—Regression Models for Ordinal Data. R package version 2019.12–10. 2019. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ordinal
-
- Dohoo I.R., Leslie K.E. Evaluation of changes in somatic cell counts as indicators of new intramammary infections. Prev. Vet. Med. 1991;10:225–237. doi: 10.1016/0167-5877(91)90006-N. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

