Application of urine C-peptide creatinine ratio in type 2 diabetic patients with different levels of renal function
- PMID: 36465621
- PMCID: PMC9712960
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1052794
Application of urine C-peptide creatinine ratio in type 2 diabetic patients with different levels of renal function
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to investigate the effect of single urine C peptide/creatinine (UCPCR) in assessing the islet β Cell function of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients with different renal function.
Methods: A total of 85 T2DM patients were recruited in this study, all the patients were assigned to one group with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR)≤60 ml·min-1·1.73 m-2 and another group complicated with eGFR>60 ml·min-1·1.73 m-2. Serum creatinine, urine creatinine, serum fasting C-peptide (FCP), fasting blood glucose (FBG), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C) and 24-hour urinary C-peptide (24hUCP) were measured. The modified homeostasis model assessment-islet β cell function [HOMA-islet (CP-DM)], the modified homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance [HOMA-IR(CP)] and UCPCR were calculated.
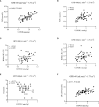
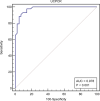
Results: When compared with group eGFR ≤60 ml·min-1·1.73 m-2, the levels of UCPCR, FCP, the modified HOMA-IR(CP) and HOMA-islet (CP-DM) were promoted and the concentrations of HbA1C, FPG, creatinine were decreased in the patients of eGFR>60 ml·min-1·1.73 m-2 (P<0.05); FCP was uncorrelated with 24hUCP while associated with UCPCR in the patients of eGFR ≤ 60 ml·min-1·1.73 m-2; UCPCR was positively correlated with FCP and HOMA-IR(CP) in the T2DM patients with different levels of renal function; the cut-off (UCPCR ≤ 1.13 nmol/g) had 88.37% sensitivity and 95.24% specificity [95% confidence interval (CI):0.919-0.997] for identifying severe insulin deficiency in T2DM patients[area under the curve (AUC) 0.978].
Conclusion: UCPCR can be used to evaluate islets β Cell function in T2DM patients with different renal function status.
Keywords: 24-hour urinary C-peptide; C peptide; EGFR; diabete; urinary C peptide/creatinine ratio.
Copyright © 2022 Zhou, Li, Yuan, Wang, Zhou, Zhang and Ye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Urinary C-peptide creatinine ratio to differentiate type 2 diabetes mellitus from type 1 in pediatric patients.Eur J Pediatr. 2020 Jul;179(7):1115-1120. doi: 10.1007/s00431-020-03606-7. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Eur J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32052124 Clinical Trial.
-
Urinary C-peptide/creatinine ratio: A useful biomarker of insulin resistance and refined classification of type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Diabetes. 2021 Nov;13(11):893-904. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13203. Epub 2021 Jun 16. J Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 34051046
-
Clinical Implications of Urinary C-Peptide Creatinine Ratio in Patients with Different Types of Diabetes.J Diabetes Res. 2019 Aug 7;2019:1747684. doi: 10.1155/2019/1747684. eCollection 2019. J Diabetes Res. 2019. PMID: 31485449 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary C-peptide and urinary C-peptide creatinine ratio as markers for insulin resistance in obese children and adolescents.Pediatr Res. 2022 Sep;92(3):805-809. doi: 10.1038/s41390-021-01847-2. Epub 2021 Nov 13. Pediatr Res. 2022. PMID: 34775475
-
Diagnostic Test Accuracy of Urine C-peptide Creatinine Ratio for the Correct Identification of the Type of Diabetes: A Systematic Review.touchREV Endocrinol. 2022 Jun;18(1):2-9. doi: 10.17925/EE.2022.18.1.2. Epub 2022 May 23. touchREV Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35949364 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Non-linear relationship between urinary creatinine and diabetic kidney disease: implications for clinical practice.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jan 24;26(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-03971-1. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39856665 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary C-Peptide to Creatinine Ratio (UCPCR) as Indicator for Metabolic Risk in Apparently Healthy Adults-A BioPersMed Cohort Study.Nutrients. 2023 Apr 25;15(9):2073. doi: 10.3390/nu15092073. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37432211 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of mulberry twig alkaloids(Sangzhi alkaloids) and metformin on blood glucose fluctuations in combination with premixed insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 2;14:1272112. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1272112. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38027146 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The predictive value of plasma uridine for type 2 diabetes and its atherosclerotic complications.Endocr Connect. 2024 May 27;13(6):e240075. doi: 10.1530/EC-24-0075. Print 2024 Jun 1. Endocr Connect. 2024. PMID: 38657664 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

