Pituitary apoplexy and COVID-19 vaccination: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 36465651
- PMCID: PMC9712198
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1035482
Pituitary apoplexy and COVID-19 vaccination: a case report and literature review
Abstract
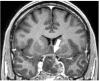
A 50-year-old man was admitted to our hospital for vomit, nausea, diplopia, and headache resistant to analgesic drugs. Symptoms started the day after his third COVID-19 mRNA vaccine (Moderna) whereas SARS-CoV-2 nasal swab was negative. Pituitary MRI showed recent bleeding in macroadenoma, consistent with pituitary apoplexy. Adverse Drug Reaction was reported to AIFA (Italian Medicines Agency).A stress dexamethasone dose was administered due to the risk of adrenal insufficiency and to reduce oedema. Biochemistry showed secondary hypogonadism; inflammatory markers were elevated as well as white blood cells count, fibrinogen and D-dimer. Pituitary tumour transsphenoidal resection was performed and pathology report was consistent with pituitary adenoma with focal haemorrhage and necrosis; we found immunohistochemical evidence for SARS-CoV-2 proteins next to pituitary capillaries, in the presence of an evident lymphocyte infiltrate.Few cases of pituitary apoplexy after COVID-19 vaccination and infection have been reported. Several hypotheses have been suggested to explain this clinical picture, including cross-reactivity between SARS-CoV-2 and pituitary proteins, COVID-19-associated coagulopathy, infection-driven acutely increased pituitary blood demand, anti-Platelet Factor 4/heparin antibodies development after vaccine administration. Ours is the first case of SARS-CoV-2 evidence in pituitary tissue, suggesting that endothelial infection of pituitary capillaries could be present before vaccination, possibly due to a previous asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Our case underlines that SARS-CoV-2 can associate with apoplexy by penetrating the central nervous system, even in cases of negative nasal swab. Patients with pituitary tumours may develop pituitary apoplexy after exposure to SARS-CoV-2, therefore clinicians should be aware of this risk.
Keywords: COVID - 19; SARS – CoV – 2; autoimmunity; pituitary apoplexy; vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT).
Copyright © 2022 Aliberti, Gagliardi, Rizzo, Bortolotti, Schiuma, Franceschetti, Gafà, Borgatti, Cavallo, Zatelli and Ambrosio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Evidences that SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine-Induced apoplexy may not be solely due to ASIA or VITT syndrome', Commentary on Pituitary apoplexy and COVID-19 vaccination: A case report and literature review.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 25;14:1111581. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1111581. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36761192 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Yousuf T, Lawrence L, Bacal A, Krikorian A. A novel association between pituitary tumor apoplexy and influenza a. AACE Clin Case Rep (2016) 2(2):e143–5. doi: 10.4158/EP15657.CR - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

