A scoping study of pulmonary paracoccidioidomycosis: severity classification based on radiographic and tomographic evaluation
- PMID: 36465893
- PMCID: PMC9704082
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2022-0053
A scoping study of pulmonary paracoccidioidomycosis: severity classification based on radiographic and tomographic evaluation
Abstract
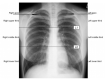
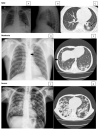
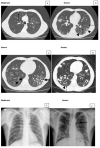
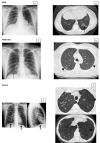
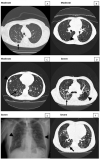
The lungs have great importance in patients with paracoccidioidomycosis since they are the portal of entry for the infecting fungi, the site of quiescent foci, and one of the most frequently affected organs. Although they have been the subject of many studies with different approaches, the severity classification of the pulmonary involvement, using imaging procedures, has not been carried out yet. This study aimed to classify the active and the residual pulmonary damage using radiographic and tomographic evaluations, according to the area involved and types of lesions.
Keywords: Paracoccidioides sp; Paracoccidioidomycosis; Radiographic evaluation; Severity classification.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Experimental paracoccidioidomycosis in the Syrian hamster: morphology, ultrastructure and correlation of lesions with presence of specific antigens and serum levels of antibodies.Mycopathologia. 1979 Jul 16;67(3):131-41. doi: 10.1007/BF00470745. Mycopathologia. 1979. PMID: 481561
-
Paracoccidioidomycosis of bones and joints. A clinical, radiologic, and pathologic study of 9 cases.Medicine (Baltimore). 1996 Jul;75(4):213-25. doi: 10.1097/00005792-199607000-00004. Medicine (Baltimore). 1996. PMID: 8699961
-
Cytokine production in lungs and adrenal glands of high and low antibody producing mice infected with Paracoccidioides brasiliensis.Med Mycol. 2006 Sep;44(6):505-14. doi: 10.1080/13693780600760781. Med Mycol. 2006. PMID: 16966167
-
Hepatic Disease with Portal Hypertension and Acute Juvenile Paracoccidioidomycosis: A Report of Two Cases and Literature Review.Mycopathologia. 2017 Oct;182(9-10):915-919. doi: 10.1007/s11046-017-0152-6. Epub 2017 Jun 2. Mycopathologia. 2017. PMID: 28577123 Review.
-
Pulmonary paracoccidioidomycosis.Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Dec;32(6):764-74. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1295724. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2011. PMID: 22167404 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of clinico-epidemiological and radiological features in paracoccidioidomycosis patients regarding serological classification using antigens from Paracoccidioides brasiliensis complex and Paracoccidioides lutzii.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Aug 25;14(8):e0008485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008485. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32841237 Free PMC article.
-
Antifungal activity of liriodenine on agents of systemic mycoses, with emphasis on the genus Paracoccidioides.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2020 Oct 28;26:e20200023. doi: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2020-0023. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 33193751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mendes RP. Paracoccidioidomycosis surveillance and control. J Venom Anim Toxins incl Trop Dis. 2010;16(2):194–197. doi: 10.1590/S1678-91992010000200003. - DOI
-
- Londero AT, Ramos CD. Paracoccidioidomycosis: a clinical and mycologic study of forty-one cases observed in Santa Maria, RS, Brazil. Am J Med. 1972;52(6):771–775. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
