Vitamin D insufficiency is high in Malaysia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies on vitamin D status in Malaysia
- PMID: 36466384
- PMCID: PMC9715981
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1050745
Vitamin D insufficiency is high in Malaysia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies on vitamin D status in Malaysia
Abstract
Purpose: To estimate the vitamin D status of participants residing in Malaysia.
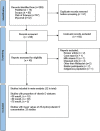
Methods: PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and MyJurnal were searched up to June 2022 without language restrictions. Studies that reported the 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] concentrations and defined their cut-off for deficiency or insufficiency from healthy participants residing in Malaysia were included. The random effects model was used to pool vitamin D status using established cut-offs of <30, <50, and <75 nmol/L according to age group.
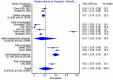
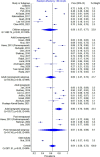
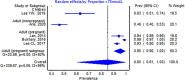
Results: From 299 studies screened, 32 studies were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled proportion for <30 nmol/L was 21% (95% CI 9-36, n = 2,438 from 10 studies), while the pooled proportion <50 nmol/L was 64% (95% CI 56-72, n = 13,977 from 30 studies), and <75 nmol/L was 85% (95% CI 61-100, n = 1,376 from five studies). Heterogeneity was high (I2 ranged from 98-99%). Higher proportions of vitamin D insufficiency (defined as <50 nmol/L) were found in participants living in the urban areas (compared to rural areas), in females (compared to males), and in Malays and Malaysian Indians (compared to Malaysian Chinese) ethnicities.
Conclusion: More than half of Malaysians have insufficient vitamin D levels, despite being a country that is close to the equator. We strongly urge prompt public health measures to improve the vitamin D status in Malaysia.
Systematic review registration: [https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/], identifier [CRD42021260259].
Keywords: 25-hydroxyvitamin D; Malaysia; cholecalciferol; prevalence; vitamin D.
Copyright © 2022 Mohd Saffian, Jamil, Mohd Tahir and Hatah.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Glob Health. 2020 Jan;8(1):e134-e142. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30457-7. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Lancet Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 31786117 Free PMC article.
-
Global and regional prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in population-based studies from 2000 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 7.9 million participants.Front Nutr. 2023 Mar 17;10:1070808. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1070808. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37006940 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of sun exposure on 25(OH) vitamin D concentration in urban and rural women in Malaysia.Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2013;22(3):391-9. doi: 10.6133/apjcn.2013.22.3.15. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23945409
-
Association between vitamin D concentration and delirium in hospitalized patients: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 8;18(2):e0281313. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281313. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36753475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk factors of vitamin D deficiency among 15-year-old adolescents participating in the Malaysian Health and Adolescents Longitudinal Research Team Study (MyHeARTs).PLoS One. 2018 Jul 19;13(7):e0200736. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200736. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30024934 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mushrooms: a food-based solution to vitamin D deficiency to include in dietary guidelines.Front Nutr. 2024 Apr 10;11:1384273. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1384273. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38660061 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D Status and Its Association With Sun Exposure in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Southern Malaysia.Cureus. 2025 Feb 27;17(2):e79747. doi: 10.7759/cureus.79747. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40161199 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Vitamin D and Its Molecular Bases in Insulin Resistance, Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome, and Cardiovascular Disease: State of the Art.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 23;24(20):15485. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015485. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D content and prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in patients with epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Nutr. 2024 Aug 30;11:1439279. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1439279. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39279896 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-ethnic proteomic profiling analysis in Alzheimer's disease identifies the disparities in dysregulation of proteins and pathogenesis.PeerJ. 2024 Jul 18;12:e17643. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17643. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39035156 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Petrelli F, Luciani A, Perego G, Dognini G, Colombelli PL, Ghidini A. Therapeutic and prognostic role of vitamin D for covid-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 observational studies. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. (2021) 211:105883. 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105883 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

