Association of mean platelet volume/lymphocyte ratio with inflammation in non-dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease stages 1-4: A retrospective study
- PMID: 36466904
- PMCID: PMC9716279
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1041356
Association of mean platelet volume/lymphocyte ratio with inflammation in non-dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease stages 1-4: A retrospective study
Abstract
Objective: The mean platelet volume/ratio (MPVLR) is recognized as a novel marker of inflammation. We evaluated whether the MPVLR is associated with inflammation in non-dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) stages 1-4.
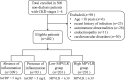
Methods: A total of 402 non-dialysis patients with CKD stages 1-4 were included. The indicators of hematological, renal function (urea, serum creatinine [Scr], estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR], and urine albumin to creatinine ratio [ACR]) and the markers of inflammation (high-sensitivity C-reactive protein [hsCRP] and fibrinogen [FIB]) were recorded. The MPVLR values at different CKD stages were analyzed. Next, based on the absence (hsCRP level < 5 mg/L) and presence (hsCRP level > 5 mg/L) of inflammation, the patients were categorized, and the differences in indices between the two groups were observed. The patients were divided into two groups based on the median MPVLR value (6.39) at admission. The laboratory indices of patients with CKD were compared. Simultaneously, a correlation analysis was performed to identify the association between the MPVLR and each parameter. A binary logistic regression analysis was performed to test whether the MPVLR was associated independently with the presence of inflammation in non-dialysis patients with CKD. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to analyzed diagnostic performance of the MPVLR in evaluating the inflammation of non-dialysis patients with CKD stages 1-4.
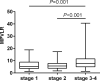
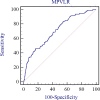
Results: The MPVLR was higher in patients with CKD stages 3-4 than in those with CKD stages 1 and 2. Significant differences in urea, Scr, eGFR, ACR, lymphocyte (LYM), red blood cell (RBC), hemoglobin (HGB), RBC distribution width (RDW-CV), MPVLR, and FIB values were observed between the groups with and without inflammation. The patients with a higher MPVLR had higher urea, Scr, ACR, WBC, neutrophils (NEU), RDW-CV, platelet distribution width (PDW), mean platelet volume (MPV), and hsCRP values and lower eGFR, LYM, RBC, HGB, and platelet (PLT) values. The MPVLR showed a positive correlation with age, urea, Scr, WBC, NEU, RDW-CV, PDW, MPV, and hsCRP values and a negative correlation with the eGFR, LYM, RBC, HGB, and PLT values. A logistic analysis revealed that the MPVLR was associated independently with the presence of inflammation in non-dialysis patients with CKD, after adjustment for the confounding factors (odds ratio = 1.020; P = 0.024). Furthermore, MPVLR exhibited a modest diagnostic performance for the assessment of inflammation in non-dialysis patients with CKD stages 1-4, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.706, and the sensitivity, specificity being 46.2% and 83.2%, respectively.
Conclusions: The MPVLR was associated independently with the presence of inflammation in non-dialysis patients with CKD and may be useful for monitoring inflammation.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; inflammation; kidney; mean platelet volume/lymphocyte ratio; non-dialysis.
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Zhang, Chen, Feng and Gan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that may be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship of mean platelet volume to lymphocyte ratio and coronary collateral circulation in patients with stable angina pectoris.Coron Artery Dis. 2017 Sep;28(6):492-497. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0000000000000530. Coron Artery Dis. 2017. PMID: 28678144
-
Mean platelet volume to lymphocyte ratio and platelet distribution width to lymphocyte ratio in Iraqi patients diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus.Reumatologia. 2022;60(3):173-182. doi: 10.5114/reum.2022.117837. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Reumatologia. 2022. PMID: 35875718 Free PMC article.
-
Mean Platelet Volume-to-Platelet Count Ratio, Mean Platelet Volume-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Red Blood Cell Distribution Width-Platelet Count Ratio as Markers of Inflammation in Patients with Ascending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm.Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2020 Apr 1;35(2):175-180. doi: 10.21470/1678-9741-2019-0348. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 32369297 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Complete Blood Count Parameters in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 23;8(2):e70488. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70488. eCollection 2025 Feb. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39995796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in the application of novel inflammatory indicators in chronic kidney disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 30;12:1500166. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1500166. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39950124 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the link: Hemogram-derived markers in type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications.World J Diabetes. 2025 Jul 15;16(7):105233. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i7.105233. World J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40697587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of white blood cell count to mean platelet volume ratio with type 2 diabetic peripheral neuropathy in a Chinese population: a cross-sectional study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2024 Jul 29;24(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01644-y. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024. PMID: 39075499 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced biomarkers for prognostic evaluation of pneumonia severity in pediatric intensive care: focus on novel inflammatory and hematological ratios.Ital J Pediatr. 2025 Jun 2;51(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s13052-025-01989-7. Ital J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40457390 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the baseline hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, and platelet (HALP) score in the United States adult population and comorbidities: an analysis of the NHANES.Front Nutr. 2023 May 18;10:1206958. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1206958. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37284646 Free PMC article.
-
The association of plasma level of phenylalanine with inflammatory markers, insulin resistance, and atherosclerotic indexes in patients with phenylketonuria.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025 May 14;24(1):119. doi: 10.1007/s40200-025-01631-7. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025. PMID: 40376305
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous