IFITM protein regulation and functions: Far beyond the fight against viruses
- PMID: 36466909
- PMCID: PMC9716219
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1042368
IFITM protein regulation and functions: Far beyond the fight against viruses
Abstract
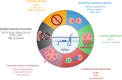
Interferons (IFNs) are important cytokines that regulate immune responses through the activation of hundreds of genes, including interferon-induced transmembrane proteins (IFITMs). This evolutionarily conserved protein family includes five functionally active homologs in humans. Despite the high sequence homology, IFITMs vary in expression, subcellular localization and function. The initially described adhesive and antiproliferative or pro-oncogenic functions of IFITM proteins were diluted by the discovery of their antiviral properties. The large set of viruses that is inhibited by these proteins is constantly expanding, as are the possible mechanisms of action. In addition to their beneficial antiviral effects, IFITM proteins are often upregulated in a broad spectrum of cancers. IFITM proteins have been linked to most hallmarks of cancer, including tumor cell proliferation, therapeutic resistance, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. Recent studies have described the involvement of IFITM proteins in antitumor immunity. This review summarizes various levels of IFITM protein regulation and the physiological and pathological functions of these proteins, with an emphasis on tumorigenesis and antitumor immunity.
Keywords: immunity; interferon-induced transmembrane proteins; stem cells; therapy resistance; tumor immunosurveillance; tumor progression.
Copyright © 2022 Friedlová, Zavadil Kokáš, Hupp, Vojtěšek and Nekulová.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ABHD16A Negatively Regulates the Palmitoylation and Antiviral Function of IFITM Proteins.mBio. 2022 Dec 20;13(6):e0228922. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02289-22. Epub 2022 Oct 31. mBio. 2022. PMID: 36314839 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Heterogeneity of Mammalian IFITM Proteins against HIV-1.J Virol. 2021 Aug 25;95(18):e0043921. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00439-21. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34160255 Free PMC article.
-
Ferret Interferon (IFN)-Inducible Transmembrane Proteins Are Upregulated by both IFN-α and Influenza Virus Infection.J Virol. 2021 Jun 24;95(14):e0011121. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00111-21. Epub 2021 Jun 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33952646 Free PMC article.
-
The Antiviral Activity of Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Proteins and Virus Evasion Strategies.Viruses. 2024 May 6;16(5):734. doi: 10.3390/v16050734. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38793616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IFITM proteins: Understanding their diverse roles in viral infection, cancer, and immunity.J Biol Chem. 2023 Jan;299(1):102741. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102741. Epub 2022 Nov 23. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 36435199 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic and Functional Evidence That miRNA193a-3p Inhibits Lymphatic Endothelial Cell (LEC) and LEC + MCF-7 Spheroid Growth Directly and by Altering MCF-7 Secretome.Cells. 2023 Jan 21;12(3):389. doi: 10.3390/cells12030389. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766731 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional epigenetic editing reveals hierarchies in gene regulation.Nat Biotechnol. 2025 Mar;43(3):355-368. doi: 10.1038/s41587-024-02213-3. Epub 2024 May 17. Nat Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38760566 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptomes of Canine and Human Prostate Cancers Identify Mediators of Castration Resistance.Vet Comp Oncol. 2024 Dec;22(4):629-640. doi: 10.1111/vco.13017. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Vet Comp Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39375962 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-stimulated genes and their antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2.mBio. 2024 Sep 11;15(9):e0210024. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02100-24. Epub 2024 Aug 22. mBio. 2024. PMID: 39171921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host cellular factors involved in pseudorabies virus attachment and entry: a mini review.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Nov 27;10:1314624. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1314624. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 38089700 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Takahashi S, Doss C, Levy S, Levy R. TAPA-1, the target of an antiproliferative antibody, is associated on the cell surface with the leu-13 antigen. J Immunol (1990) 145:2207–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

