Validation of the Remote Automated ki:e Speech Biomarker for Cognition in Mild Cognitive Impairment: Verification and Validation following DiME V3 Framework
- PMID: 36466952
- PMCID: PMC9710455
- DOI: 10.1159/000526471
Validation of the Remote Automated ki:e Speech Biomarker for Cognition in Mild Cognitive Impairment: Verification and Validation following DiME V3 Framework
Abstract
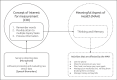
Introduction: Progressive cognitive decline is the cardinal behavioral symptom in most dementia-causing diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. While most well-established measures for cognition might not fit tomorrow's decentralized remote clinical trials, digital cognitive assessments will gain importance. We present the evaluation of a novel digital speech biomarker for cognition (SB-C) following the Digital Medicine Society's V3 framework: verification, analytical validation, and clinical validation.
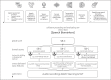
Methods: Evaluation was done in two independent clinical samples: the Dutch DeepSpA (N = 69 subjective cognitive impairment [SCI], N = 52 mild cognitive impairment [MCI], and N = 13 dementia) and the Scottish SPeAk datasets (N = 25, healthy controls). For validation, two anchor scores were used: the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) and the Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) scale.
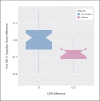
Results: Verification: The SB-C could be reliably extracted for both languages using an automatic speech processing pipeline. Analytical Validation: In both languages, the SB-C was strongly correlated with MMSE scores. Clinical Validation: The SB-C significantly differed between clinical groups (including MCI and dementia), was strongly correlated with the CDR, and could track the clinically meaningful decline.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that the ki:e SB-C is an objective, scalable, and reliable indicator of cognitive decline, fit for purpose as a remote assessment in clinical early dementia trials.
Keywords: Clinical trials; Dementia; Digital biomarker; Mild cognitive impairment; Speech analysis; Speech biomarker.
Copyright © 2022 by The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Daphne ter Huurne, Nina Possemis, and Inez Ramakers have no conflicts of interest. Johannes Tröger, Ebru Baykara, Jian Zhao, Elisa Mallick, Simona Schäfer, Louisa Schwed, Mario Mina, and Nicklas Linz are employees of the digital biomarker company ki elements. Johannes Tröger and Nicklas Linz hold shares of the digital biomarker company ki elements. Craig Ritchie has received consultancy fees from Biogen, Eisai, MSD, Actinogen, Roche, and Eli Lilly, as well as payment or honoraria from Roche and Eisai.
Figures


References
-
- McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack CR, Kawas CH, et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011 May;7((3)):263–269. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

