Activation of EP4 alleviates AKI-to-CKD transition through inducing CPT2-mediated lipophagy in renal macrophages
- PMID: 36467025
- PMCID: PMC9709464
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1030800
Activation of EP4 alleviates AKI-to-CKD transition through inducing CPT2-mediated lipophagy in renal macrophages
Abstract
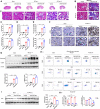
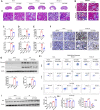
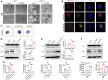
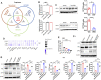
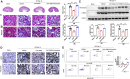
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common clinical syndrome with complex pathogenesis, characterized by a rapid decline in kidney function in the short term. Worse still, the incomplete recovery from AKI increases the risk of progression to chronic kidney disease (CKD). However, the pathogenesis and underlying mechanism remain largely unknown. Macrophages play an important role during kidney injury and tissue repair, but its role in AKI-to-CKD transition remains elusive. Herein, single nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-Seq) and flow cytometry validations showed that E-type prostaglandin receptor 4 (EP4) was selectively activated in renal macrophages, rather than proximal tubules, in ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI)-induced AKI-to-CKD transition mouse model. EP4 inhibition aggravated AKI-to-CKD transition, while EP4 activation impeded the progression of AKI to CKD though regulating macrophage polarization. Mechanistically, network pharmacological analysis and subsequent experimental verifications revealed that the activated EP4 inhibited macrophage polarization through inducing Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2 (CPT2)-mediated lipophagy in macrophages. Further, CPT2 inhibition abrogated the protective effect of EP4 on AKI-to-CKD transition. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that EP4-CPT2 signaling-mediated lipophagy in macrophages plays a pivotal role in the transition of AKI to CKD and targeting EP4-CPT2 axis could serve as a promising therapeutic approach for retarding AKI and its progression to CKD.
Keywords: AKI-to-CKD transition; CPT2; EP4; lipophagy; macrophages.
Copyright © 2022 Guan, Liu, Xin, Qin, Gong, Xiao, Zhang, Li, Xiong, Yang, He, Zhao and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Blockade of STAT3 signaling alleviates the progression of acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease through antiapoptosis.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022 May 1;322(5):F553-F572. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00595.2020. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35311382
-
Cell Profiling of Acute Kidney Injury to Chronic Kidney Disease Reveals Novel Oxidative Stress Characteristics in the Failed Repair of Proximal Tubule Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 18;24(14):11617. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411617. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511374 Free PMC article.
-
Poricoic acid A enhances melatonin inhibition of AKI-to-CKD transition by regulating Gas6/AxlNFκB/Nrf2 axis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Apr;134:484-497. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.01.046. Epub 2019 Feb 2. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30716432
-
Driving role of macrophages in transition from acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease.Chin Med J (Engl). 2022 Apr 5;135(7):757-766. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002100. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022. PMID: 35671177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PTEN in kidney diseases: a potential therapeutic target in preventing AKI-to-CKD transition.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 6;11:1428995. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1428995. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39165377 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Arachidonic acid metabolism as a therapeutic target in AKI-to-CKD transition.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 8;15:1365802. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1365802. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38523633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The crucial role of metabolic reprogramming in driving macrophage conversion in kidney disease.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jun 16;30(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00746-2. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40524149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate Signaling in Chronic Kidney Disease: Molecular Targets and Therapeutic Potentials.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 30;25(17):9441. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179441. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic characterisation of perhexiline treatment on THP-1 M1 macrophage differentiation.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 13;14:1054588. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1054588. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36993962 Free PMC article.
-
Role of G protein coupled receptors in acute kidney injury.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Sep 2;22(1):423. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01802-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39223553 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

