Emerging pharmaceutical therapeutics and delivery technologies for osteoarthritis therapy
- PMID: 36467045
- PMCID: PMC9712996
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.945876
Emerging pharmaceutical therapeutics and delivery technologies for osteoarthritis therapy
Abstract
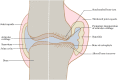
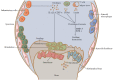
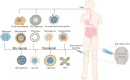
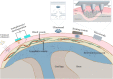
Osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the most common joint degenerative diseases in the world. At present, the management of OA depends on the lifestyle modification and joint replacement surgery, with the lifespan of prosthesis quite limited yet. Effective drug treatment of OA is essential. However, the current drugs, such as the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and acetaminophen, as well as glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid, are accompanied by obvious side effects, with the therapeutic efficacy to be enhanced. Recently, novel reagents such as IL-1 antagonists and nerve growth factor inhibitors have entered clinical trials. Moreover, increasing evidence demonstrated that active ingredients of natural plants have great potential for treating OA. Meanwhile, the use of novel drug delivery strategies may overcome the shortcomings of conventional preparations and enhance the bioavailability of drugs, as well as decrease the side effects significantly. This review therefore summarizes the pathological mechanisms, management strategies, and research progress in the drug molecules including the newly identified active ingredient derived from medicinal plants for OA therapy, with the drug delivery technologies also summarized, with the expectation to provide the summary and outlook for developing the next generation of drugs and preparations for OA therapy.
Keywords: delivery technologies; drug candidates; osteoarthritis; pathological mechanism; treatment strategies.
Copyright © 2022 Shentu, Yan, Xu, Chen and Peng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Progress and Challenges of Topical Delivery Technologies Meditated Drug Therapy for Osteoarthritis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Aug 14;19:8337-8352. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S466437. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39161359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intra-articular viscosupplementation with hylan g-f 20 to treat osteoarthritis of the knee: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005;5(10):1-66. Epub 2005 Jun 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005. PMID: 23074461 Free PMC article.
-
Current Treatment Options for Osteoarthritis.Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2018;14(2):108-116. doi: 10.2174/1573397113666170829155149. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2018. PMID: 28875826 Review.
-
Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate as therapeutic agents for knee and hip osteoarthritis.Drugs Aging. 2007;24(7):573-80. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200724070-00005. Drugs Aging. 2007. PMID: 17658908 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of glucosamine sulfate in the management of osteoarthritis: Evidence from real-life setting trials and surveys.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016 Feb;45(4 Suppl):S12-7. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.11.011. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016. PMID: 26806187 Review.
Cited by
-
Global burden of osteoarthritis in adults aged 30 to 44 years, 1990 to 2019: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Apr 19;25(1):303. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07442-w. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38641788 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of T1p Characteristics of Load-Bearing Hip Cartilage on Bilateral Knee Patellar Cartilage Subregions: Subjects With None to Moderate Radiographic Hip Osteoarthritis.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024 Jul;60(1):186-202. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29009. Epub 2023 Sep 13. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024. PMID: 37702305 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Synergistic Anti-inflammatory and Joint Protection Effects for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment.Pharm Res. 2024 Jul;41(7):1493-1505. doi: 10.1007/s11095-024-03732-z. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 38918308
-
Overexpression of RAD54L attenuates osteoarthritis by suppressing the HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway: Bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 9;19(4):e0298575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298575. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38593124 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of lncRNAs in osteoarthritis development and potential therapy.Front Genet. 2023 Sep 14;14:1273933. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1273933. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37779916 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ayral X., Pickering E. H., Woodworth T. G., Mackillop N., Dougados M. (2005). Synovitis: A potential predictive factor of structural progression of medial tibiofemoral knee osteoarthritis -- results of a 1 year longitudinal arthroscopic study in 422 patients. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 13, 361–367. 10.1016/j.joca.2005.01.005 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources