The relationship among idiosyncratic deals, psychological empowerment, and internal locus of control: A moderated mediation model
- PMID: 36467215
- PMCID: PMC9710624
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.923874
The relationship among idiosyncratic deals, psychological empowerment, and internal locus of control: A moderated mediation model
Abstract
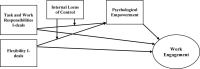
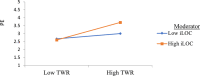
Building upon the job demands-resources (JD-R) theory, this research offers an in-depth exploration of the mechanisms by which idiosyncratic deals (I-deals), such as personalized work arrangements, can enhance academics' psychological empowerment (PE) and hence affect their work engagement. This study's purpose was to investigate whether PE mediates the relationships between task and work responsibilities I-deals, flexibility I-deals, and work engagement among academics in higher education and whether the mediating effects are moderated by academics' internal locus of control. Using an online platform, the survey questionnaire was sent to 650 academics working in higher education. The results reveal that task and work responsibilities I-deals and flexibility I-deals, are positively associated with the academics' work engagement and that PE mediates those relationships. Additionally, the internal locus of control strengthens the positive relationship between task and work responsibilities I-deals and PE, and it enhances the indirect effect of task and work responsibilities I-deals on academics' work engagement through PE. Though, this study did not find the moderating effect of internal locus of control on the flexibility I-deals-PE relationship; however, the results indicate that internal locus of control boosts the indirect effect of flexibility I-deals on academics' work engagement through PE.
Keywords: higher education; idiosyncratic deals; internal locus of control; psychological empowerment; work engagement.
Copyright © 2022 Shams, Mei, Adnan, Niazi and Khan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
How psychological empowerment impacts task performance: The mediation role of work engagement and moderating role of age.Front Psychol. 2022 Sep 16;13:889936. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.889936. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36186278 Free PMC article.
-
Job Demands, Resources, and Future Considerations: Academics' Experiences of Working From Home During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic.Front Psychol. 2022 Jun 21;13:908640. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.908640. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35832908 Free PMC article.
-
Workplace empowerment, psychological empowerment and work-related wellbeing in southeast Asian employees: a cross-sectional survey.Health Promot Int. 2022 Aug 1;37(4):daac113. doi: 10.1093/heapro/daac113. Health Promot Int. 2022. PMID: 36102476
-
What do we know about university academics' mental health? A systematic literature review.Stress Health. 2020 Dec;36(5):563-585. doi: 10.1002/smi.2956. Epub 2020 Jul 4. Stress Health. 2020. PMID: 32407607
-
The Transition to Retirement Experiences of Academics in "Higher Education": A Meta-Ethnography.Gerontologist. 2019 May 17;59(3):e177-e195. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnx206. Gerontologist. 2019. PMID: 29385494 Review.
References
-
- Aboramadan M., Albashiti B., Alharazin H., Dahleez K. A. (2019). Human resources management practices and organizational commitment in higher education: The mediating role of work engagement. Int. J. Educ. Manage. 34 154–174. 10.1108/IJEM-04-2019-0160 - DOI
-
- Aboramadan M., Dahleez K., Hamad M. (2020). Servant leadership and academics’ engagement in higher education: mediation analysis. J. Higher Educ. Policy Manag. 42 617–633. 10.1080/1360080x.2020.1774036 - DOI
-
- Akca F., Ulutas E., Yabanci C. (2018). Investigation of teachers’ self-efficacy beliefs, locus of control and intercultural sensitivities from the perspective of individual differences. J. Educ. Learn. 7 219–232. 10.5539/jel.v7n3p219 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources