Self-Expanding Metallic Stents for Palliation of Esophageal Cancer: A Single Center Experience From Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 36467426
- PMCID: PMC9713855
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.32096
Self-Expanding Metallic Stents for Palliation of Esophageal Cancer: A Single Center Experience From Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Background: Self-expanding metallic stents (SEMSs) are increasingly used as a non-surgical alternative for the palliation of advanced esophageal cancer (EC). However, there is a scarcity of real-life experience with the use of these stents exclusively in EC. The aim of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of SEMS in inoperable ECs in the western region of Saudi Arabia.
Methods: A retrospective review of SEMS placed in a tertiary referral hospital for histologically proven inoperable EC from 2016 to 2019. Demographics data, procedure success, complication, re-intervention, and mortality were analyzed.
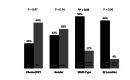
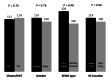
Results: Forty-eight SEMS placed in 35 patients for palliation of dysphagia. The median age of patients was 68 years (range 31-95). 69% (24) patients have a lower third of EC and the rest have a middle third. SEMSs were placed successfully in all cases with symptomatic improvement. No major stent-related complication was seen. 28% (13) patients required re-intervention with additional SEMS placement, nine of which were for tissue in growth and four for distal migration. Median survival was 114 days (range 30-498). Most of the complications seen in fully covered SEMS compared to the partially covered 50% (8/16) vs 17% (5/30), respectively, p = 0.04. Chemo and/or radiotherapy were given to 51% (18) of the patients without any significant benefit on survival (p = 0.79) or re-intervention rate (p = 0.47) compared to those who did not.
Conclusion: SEMS is effective in palliating dysphagia in inoperable EC without major complications. Rates of tumors in growth and migration were comparable to other studies. SEMS provides long-term palliation.
Keywords: cancer; ec- esophageal cancer; gastroenterology; palliation; self-expanding metallic stent.
Copyright © 2022, Alzanbagi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Outcome of palliative esophageal stenting for malignant dysphagia: a retrospective analysis. Burstow M, Kelly T, Panchani S, Khan IM, Meek D, Memon B, Memon MA. Dis Esophagus. 2009;22:519–525. - PubMed
-
- Novel stent in the palliation of malignant esophageal strictures: a retrospective study. Chen H, Ni Z, Jing D, et al. Dis Esophagus. 2017;30:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Self-expanding metal stents in the palliation of malignant dysphagia: outcome analysis in 100 consecutive patients. Elphick DA, Smith BA, Bagshaw J, Riley SA. Dis Esophagus. 2005;18:93–95. - PubMed
-
- The use of self-expandable metallic stents for palliative treatment of inoperable esophageal cancer. Eroglu A, Turkyilmaz A, Subasi M, Karaoglanoglu N. Dis Esophagus. 2010;23:64–70. - PubMed
-
- Development of a prediction model of adverse events after stent placement for esophageal cancer. Fuccio L, Scagliarini M, Frazzoni L, Battaglia G. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;83:746–752. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
