Juvenile Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Identification of Novel Central Neuroinflammation Biomarkers
- PMID: 36469191
- PMCID: PMC9957825
- DOI: 10.1007/s10875-022-01407-1
Juvenile Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Identification of Novel Central Neuroinflammation Biomarkers
Abstract
Introduction: Juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus (j-SLE) is a rare chronic autoimmune disease affecting multiple organs. Ranging from minor features, such as headache or mild cognitive impairment, to serious and life-threatening presentations, j-neuropsychiatric SLE (j-NPSLE) is a therapeutic challenge. Thus, the diagnosis of NPSLE remains difficult, especially in pediatrics, with no specific biomarker of the disease yet validated.
Objectives: To identify central nervous system (CNS) disease biomarkers of j-NPSLE.
Methods: A 5-year retrospective tertiary reference monocentric j-SLE study. A combination of standardized diagnostic criteria and multidisciplinary pediatric clinical expertise was combined to attribute NP involvement in the context of j-SLE. Neopterin and interferon-alpha (IFN-α) protein levels in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) were assessed, together with routine biological and radiological investigations.
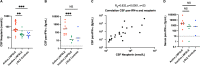
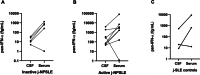
Results: Among 51 patients with j-SLE included, 39% presented with j-NPSLE. J-NPSLE was diagnosed at onset of j-SLE in 65% of patients. No specific routine biological or radiological marker of j-NPSLE was identified. However, CSF neopterin levels were significantly higher in active j-NPSLE with CNS involvement than in j-SLE alone (p = 0.0008). Neopterin and IFN-α protein levels in CSF were significantly higher at diagnosis of j-NPSLE with CNS involvement than after resolution of NP features (respectively p = 0.0015 and p = 0.0010) upon immunosuppressive treatment in all patients tested (n = 10). Both biomarkers correlated strongly with each other (Rs = 0.832, p < 0.0001, n = 23 paired samples).
Conclusion: CSF IFN-α and neopterin constitute promising biomarkers useful in the diagnosis and monitoring of activity in j-NPSLE.
Keywords: Biomarker; Central nervous system; Interferon-alpha; Juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus; Neopterin; Neuropsychiatric.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sibbitt WL, Brandt JR, Johnson CR, Maldonado ME, Patel SR, Ford CC, et al. The incidence and prevalence of neuropsychiatric syndromes in pediatric onset systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2002;29(7):1536–1542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

