CCN2/CTGF promotes liver fibrosis through crosstalk with the Slit2/Robo signaling
- PMID: 36469291
- PMCID: PMC10030765
- DOI: 10.1007/s12079-022-00713-y
CCN2/CTGF promotes liver fibrosis through crosstalk with the Slit2/Robo signaling
Abstract
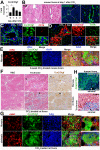
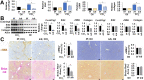
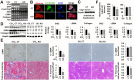
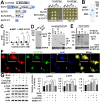
Liver fibrosis is the common outcome of many chronic liver diseases, resulting from altered cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions that promote hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation and excessive matrix production. This study aimed to investigate functions of cellular communication network factor 2 (CCN2)/Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), an extracellular signaling modulator of the CYR61/CTGF/Nov (CCN) family, in liver fibrosis. Tamoxifen-inducible conditional knockouts in mice and hepatocyte-specific deletion of this gene in rats were generated using the Cre-lox system. These animals were subjected to peri-central hepatocyte damage caused by carbon tetrachloride. Potential crosstalk of this molecule with a new profibrotic pathway mediated by the Slit2 ligand and Roundabout (Robo) receptors was also examined. We found that Ccn2/Ctgf was highly upregulated in periportal hepatocytes during carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatocyte damage, liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in mice and rats. Overexpression of this molecule was observed in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) that were surrounded with fibrotic cords. Deletion of the Ccn2/Ctgf gene significantly reduced expression of fibrosis-related genes including Slit2, a smooth muscle actin (SMA) and Collagen type I during carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice and rats. In addition, Ccn2/Ctgf and its truncated mutant carrying the first three domains were able to interact with the 7th -9th epidermal growth factor (EGF) repeats and the C-terminal cysteine knot (CT) motif of Slit2 protein in cultured HSC and fibrotic murine livers. Ectopic expression of Ccn2/Ctgf protein upregulated Slit2, promoted HSC activation, and potentiated fibrotic responses following chronic intoxication by carbon tetrachloride. Moreover, Ccn2/Ctgf and Slit2 synergistically enhanced activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and AKT in primary HSC, whereas soluble Robo1-Fc chimera protein could inhibit these activities. These observations demonstrate conserved cross-species functions of Ccn2/Ctgf protein in rodent livers. This protein can be induced in hepatocytes and contribute to liver fibrosis. Its novel connection with the Slit2/Robo signaling may have therapeutic implications against fibrosis in chronic liver disease.
Keywords: Carbon tetrachloride; Cellular communication network factor 2 (CCN2)/Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF); Hepatic stellate cells; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Liver fibrosis; Robo1; Slit2.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of Slit2-Robo1 signaling promotes liver fibrosis.J Hepatol. 2015 Dec;63(6):1413-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.07.033. Epub 2015 Aug 8. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26264936
-
Taurocholate Induces Connective Tissue Growth Factor Expression in Hepatocytes Through ERK-YAP Signaling.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(5):1711-1725. doi: 10.1159/000494790. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30384360
-
Susceptibility to liver fibrosis in mice expressing a connective tissue growth factor transgene in hepatocytes.Hepatology. 2009 Sep;50(3):939-47. doi: 10.1002/hep.23102. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19670427 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of hepatic stellate cells by connective tissue growth factor.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012 Jun 1;17(7):2495-507. doi: 10.2741/4067. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012. PMID: 22652794 Review.
-
Significance of CCNs in liver regeneration.J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Jun;17(2):321-332. doi: 10.1007/s12079-023-00762-x. Epub 2023 May 18. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37202628 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Liver Fibrosis Resolution: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Opportunities.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 2;24(11):9671. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119671. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Exosomal Modulation of Macrophages in Liver Fibrosis.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2024 Feb 28;12(2):201-209. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2023.00381. Epub 2023 Nov 23. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38343615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of the Wnt signaling pathway and its role in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and hepatic fibrosis in alveolar echinococcosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 May 27;15:1583802. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1583802. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40496021 Free PMC article.
-
The SLIT/ROBO Pathway in Liver Fibrosis and Cancer.Biomolecules. 2023 May 1;13(5):785. doi: 10.3390/biom13050785. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37238655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and biological function of the cellular communication network factor 5 (CCN5) in primary liver cells.J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Jun;17(2):307-320. doi: 10.1007/s12079-023-00757-8. Epub 2023 May 11. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37166689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coll M, Arino S, Martinez-Sanchez C, Garcia-Pras E, Gallego J, Moles A, Aguilar-Bravo B, Blaya D, Vallverdu J, Rubio-Tomas T, Lozano JJ, Pose E, Graupera I, Fernandez-Vidal A, Pol A, Bataller R, Geng JG, Gines P, Fernandez M, Sancho-Bru P (2022) Ductular reaction promotes intrahepatic angiogenesis through Slit2-Roundabout 1 signaling. Hepatology 75:353 – 68 - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

