Computed Tomographic Radiomics in Differentiating Histologic Subtypes of Epithelial Ovarian Carcinoma
- PMID: 36469315
- PMCID: PMC9855300
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.45141
Computed Tomographic Radiomics in Differentiating Histologic Subtypes of Epithelial Ovarian Carcinoma
Abstract
Importance: Epithelial ovarian carcinoma is heterogeneous and classified according to the World Health Organization Tumour Classification, which is based on histologic features and molecular alterations. Preoperative prediction of the histologic subtypes could aid in clinical management and disease prognostication.
Objective: To assess the value of radiomics based on contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) in differentiating histologic subtypes of epithelial ovarian carcinoma in multicenter data sets.
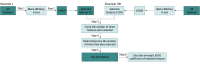
Design, setting, and participants: In this diagnostic study, 665 patients with histologically confirmed epithelial ovarian carcinoma were retrospectively recruited from 4 centers (Hong Kong, Guangdong Province of China, and Seoul, South Korea) between January 1, 2012, and February 28, 2022. The patients were randomly divided into a training cohort (n = 532) and a testing cohort (n = 133) with a ratio of 8:2. This process was repeated 100 times. Tumor segmentation was manually delineated on each section of contrast-enhanced CT images to encompass the entire tumor. The Mann-Whitney U test and voted least absolute shrinkage and selection operator were performed for feature reduction and selection. Selected features were used to build the logistic regression model for differentiating high-grade serous carcinoma and non-high-grade serous carcinoma.
Exposures: Contrast-enhanced CT-based radiomics.
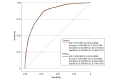
Main outcomes and measures: Intraobserver and interobserver reproducibility of tumor segmentation were measured by Dice similarity coefficients. The diagnostic efficiency of the model was assessed by receiver operating characteristic curve and area under the curve.
Results: In this study, 665 female patients (mean [SD] age, 53.6 [10.9] years) with epithelial ovarian carcinoma were enrolled and analyzed. The Dice similarity coefficients of intraobserver and interobserver were all greater than 0.80. Twenty radiomic features were selected for modeling. The areas under the curve of the logistic regression model in differentiating high-grade serous carcinoma and non-high-grade serous carcinoma were 0.837 (95% CI, 0.835-0.838) for the training cohort and 0.836 (95% CI, 0.833-0.840) for the testing cohort.
Conclusions and relevance: In this diagnostic study, radiomic features extracted from contrast-enhanced CT were useful in the classification of histologic subtypes in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Intraobserver and interobserver reproducibility of tumor segmentation was excellent. The proposed logistic regression model offered excellent discriminative ability among histologic subtypes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Contrast-enhanced CT radiomics for preoperative prediction of stage in epithelial ovarian cancer: a multicenter study.BMC Cancer. 2024 Mar 6;24(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12037-8. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38448945 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of radiomics nomogram for metastatic status of epithelial ovarian cancer.Sci Rep. 2024 May 30;14(1):12456. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63369-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38816463 Free PMC article.
-
Computed tomography-based radiomics machine learning classifiers to differentiate type I and type II epithelial ovarian cancers.Eur Radiol. 2023 Jul;33(7):5193-5204. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-09318-w. Epub 2022 Dec 14. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36515713
-
Seeing beyond the tumor: computed tomography image-based radiomic analysis helps identify ovarian clear cell carcinoma subtype in epithelial ovarian cancer.Radiol Med. 2023 Aug;128(8):900-911. doi: 10.1007/s11547-023-01666-x. Epub 2023 Jun 27. Radiol Med. 2023. PMID: 37368228
-
Integration of proteomics with CT-based qualitative and radiomic features in high-grade serous ovarian cancer patients: an exploratory analysis.Eur Radiol. 2020 Aug;30(8):4306-4316. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06755-3. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32253542 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Contrast-enhanced CT radiomics for preoperative prediction of stage in epithelial ovarian cancer: a multicenter study.BMC Cancer. 2024 Mar 6;24(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12037-8. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38448945 Free PMC article.
-
A CT-based radiomics model for predicting progression-free survival in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer.BMC Cancer. 2025 May 20;25(1):899. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14265-y. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40394512 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning radiomics nomogram for preoperatively identifying moderate-to-severe chronic cholangitis in children with pancreaticobiliary maljunction: a multicenter study.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Feb 5;25(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01579-3. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39910477 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative deep learning and radiomics analysis for ovarian tumor classification and diagnosis: a multicenter large-sample comparative study.Radiol Med. 2025 Jun;130(6):889-904. doi: 10.1007/s11547-025-02006-x. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Radiol Med. 2025. PMID: 40167932
-
Validity of a multiphase CT-based radiomics model in predicting the Leibovich risk groups for localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma: an exploratory study.Insights Imaging. 2023 Oct 10;14(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s13244-023-01526-2. Insights Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37816901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kurman RJ. WHO Classification of Tumours of Female Reproductive Organs. International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2014.

