Genetic and demographic signatures accompanying the evolution of the selfing syndrome in Daphne kiusiana, an evergreen shrub
- PMID: 36469429
- PMCID: PMC10184445
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcac142
Genetic and demographic signatures accompanying the evolution of the selfing syndrome in Daphne kiusiana, an evergreen shrub
Abstract
Background and aims: The evolution of mating systems from outcrossing to self-fertilization is a common transition in flowering plants. This shift is often associated with the 'selfing syndrome', which is characterized by less visible flowers with functional changes to control outcrossing. In most cases, the evolutionary history and demographic dynamics underlying the evolution of the selfing syndrome remain poorly understood.
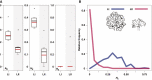
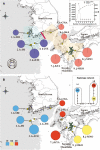
Methods: Here, we characterize differences in the demographic genetic consequences and associated floral-specific traits between two distinct geographical groups of a wild shrub, Daphne kiusiana, endemic to East Asia; plants in the eastern region (southeastern Korea and Kyushu, Japan) exhibit smaller and fewer flowers compared to those of plants in the western region (southwestern Korea). Genetic analyses were conducted using nuclear microsatellites and chloroplast DNA (multiplexed phylogenetic marker sequencing) datasets.
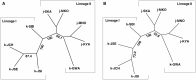
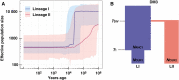
Key results: A high selfing rate with significantly increased homozygosity characterized the eastern lineage, associated with lower levels of visibility and herkogamy in the floral traits. The two lineages harboured independent phylogeographical histories. In contrast to the western lineage, the eastern lineage showed a gradual reduction in the effective population size with no signs of a severe bottleneck despite its extreme range contraction during the last glacial period.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that the selfing-associated morphological changes in D. kiusiana are of relatively old origin (at least 100 000 years ago) and were driven by directional selection for efficient self-pollination. We provide evidence that the evolution of the selfing syndrome in D. kiusiana is not strongly associated with a severe population bottleneck.
Keywords: Daphne kiusiana; NGS technique; demographic dynamics; directional selection; evergreen shrub; inflorescence; selfing syndrome.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Annals of Botany Company.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Comment in
-
Did Late Quaternary climate change trigger shifts in mating system in temperate plant species of the Sino-Japanese Floristic Region? A commentary on 'Genetic and demographic signatures accompanying the evolution of the selfing syndrome in Daphne kiusiana, an evergreen shrub'.Ann Bot. 2023 May 15;131(5):iii-v. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcad026. Ann Bot. 2023. PMID: 36869730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarez-Solas J, Banderas R, Robinson A, Montoya M.. 2019. Ocean-driven millennial-scale variability of the Eurasian ice sheet during the last glacial period simulated with a hybrid ice-sheet–shelf model. Climate of the Past 15: 957–979. doi:10.5194/cp-15-957-2019. - DOI
-
- Baker HG. 1955. Self-compatibility and establishment after ‘long-distance’ dispersal. Evolution 9: 347–349. doi:10.2307/2405656. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

