Bioimpedanciometry in nutritional and hydration assessments in a single dialysis center
- PMID: 36469485
- PMCID: PMC10697165
- DOI: 10.1590/2175-8239-JBN-2022-0037en
Bioimpedanciometry in nutritional and hydration assessments in a single dialysis center
Abstract
Background: Bioimpedance analysis (BIA) has been demonstrated to add accuracy to nutritional and volume status assessments in dialysis (HD) patients.
Aim: to describe a sample of dialysis patients from a single center on their demographics and BIA of volume distribution and nutritional status, and mortality during 12-month follow-up.
Methods: prospective observational cohort study to evaluate vintage HD patients with single-frequency BIA.
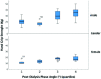
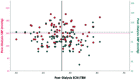
Results: we evaluated 82 patients, 29% over 65 years old. Elderly patients had higher ECW/TBW (0.51 vs. 0.44, p < 0.0001), and narrower phase angle (PhA) (4.9 vs. 6.4º, p < 0.0001). Fifteen patients (18.2%) died during follow-up, eight (53%) were elderly. Death was associated with age (62.6 vs. 50.2 years, p = 0.012), post-HD PhA (4.8 vs. 6.2º, p = 0.0001), and post-HD ECW/TBW (0.50 vs. 0.45, p = 0.015). The ROC curve analysis to predict mortality found ECW/TBW ≥ 0.47 and PhA ≤ 5.5º to have the best sensitivity and specificity. One-year patient survival was lower with post-HD ECW/TBW ≥ 0.47 (69.5% vs. 90.6%, p = 0.019), age ≥ 65 years (64.2%, vs. 86.2%, p = 0.029), and PhA ≤ 5.5º (68.2 vs. 91.0%, p = 0.002). Cox regression analysis demonstrated that PhA [HR 5.04 (95%CI 1.60-15.86), p = 0.006] remained associated with death after adjusting for age and ECW/TBW.
Conclusion: BIA is useful in assessing volume distribution and nutrition in HD patients, and combined with clinical judgement, may help determine dry weight, especially in elderly patients. Narrower PhA and higher ECW/TBW after HD were associated with poorer one-year survival.
Antecedentes:: Análise de bioimpedância (BIA) demonstrou adicionar acurácia às avaliações de estado nutricional e de volume em pacientes em diálise (HD).
Objetivo:: descrever amostra de pacientes em diálise de um único centro quanto aos aspectos demográficos e BIA na distribuição de volume e no estado nutricional, e a mortalidade em 12 meses de acompanhamento.
Métodos:: estudo de coorte observacional prospectivo para avaliar pacientes prevalentes em HD com BIA de frequência única.
Resultados:: avaliamos 82 pacientes, 29% acima de 65 anos. Pacientes idosos apresentaram maior AEC/ACT (0,51 vs. 0,44; p < 0,0001), e ângulo de fase mais estreito (PhA) (4,9 vs. 6,4º; p < 0,0001). Quinze pacientes (18,2%) foram a óbito durante acompanhamento, oito (53%) eram idosos. Óbito foi associado à idade (62,6 vs. 50,2 anos, p = 0,012), PhA pós-HD (4,8 vs. 6,2º; p = 0,0001), e AEC/ACT pós-HD (0,50 vs. 0,45, p = 0,015). A análise da curva ROC para prever mortalidade constatou que AEC/ACT ≥ 0,47 e PhA ≤ 5,5º apresentam melhor sensibilidade e especificidade. Sobrevida do paciente em um ano foi menor com AEC/ACT pós-HD ≥ 0,47 (69,5% vs. 90,6%; p = 0,019), idade ≥ 65 anos (64,2% vs. 86,2%; p = 0,029), e PhA ≤ 5,5º (68,2 vs. 91,0%; p = 0,002). A análise de regressão de Cox demonstrou que PhA [HR 5,04 (IC 95% 1,60–15,86); p = 0,006] permaneceu associado ao óbito após ajuste para idade e AEC/ACT.
Conclusão:: BIA é útil ao avaliar distribuição de volume e nutrição em pacientes em HD, e juntamente com julgamento clínico, pode ajudar a determinar o peso seco, principalmente em pacientes idosos. PhA mais estreito e maior AEC/ACT pós-HD foram associados a pior sobrevida em um ano.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Onofriescu M, Hogas S, Voroneanu L, Apetrii M, Nistor I, Kanbay M, et al. Bioimpedance-guided fluid management in maintenance hemodialysis: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;64(1):111–8. 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.01.420 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wabel P, Chamney P, Moissl U, Jirka T. Importance of whole-body bioimpedance spectroscopy for the management of fluid balance. Blood Purif. 2009;27(1):75–80. 10.1159/000167013 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tonelli M, Wiebe N, Culleton B, House AA, Rabbat C, Fok M, et al. Chronic kidney disease and mortality risk: a systematic review. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(7):2034–47. 10.1681/ASN.2005101085 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wizemann V, Wabel P, Chamney P, Zaluska W, Moissl U, Rode C, et al. The mortality risk of overhydration in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24(5):1574–9. 10.1093/ndt/gfn707 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Passauer J, Petrov H, Schleser A, Leicht J, Pucalka K. Evaluation of clinical dry weight assessment in haemodialysis patients using bioimpedance spectroscopy: a cross-sectional study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25(2):545–51. 10.1093/ndt/gfp517 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

