Shorter telomere length and suicidal ideation in familial bipolar disorder
- PMID: 36469522
- PMCID: PMC9721487
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275999
Shorter telomere length and suicidal ideation in familial bipolar disorder
Abstract
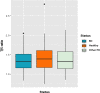
Bipolar Disorder (BD) has recently been related to a process of accelerated aging, with shortened leukocyte telomere length (LTL) in this population. It has also been observed that the suicide rate in BD patients is higher than in the general population, and more recently the telomere length variation has been described as shorter in suicide completers compared with control subjects. Objectives The aim of the present study was to investigate if there is an association between LTL and BD in families where two or more members have BD including clinical symptomatology variables, along with suicide behavior. Methods Telomere length and single copy gene ratio (T/S ratio) was measured using quantitative polymerase chain reaction in a sample of 143 relatives from 22 families, of which 60 had BD. The statistical analysis was performed with a polygenic mixed model. Results LTL was associated with suicidal ideation (p = 0.02) as that there is an interaction between suicidal ideation and course of the disorder (p = 0.02). The estimated heritability for LTL in these families was 0.68. In addition, covariates that relate to severity of disease, i.e. suicidal ideation and course of the disorder, showed an association with shorter LTL in BD patients. No difference in LTL between BD patients and healthy relatives was observed. Conclusion LTL are shorter in subjects with familial BD suggesting that stress related sub-phenotypes possibly accelerate the process of cellular aging and correlate with disease severity and suicidal ideation.
Copyright: © 2022 Martinez et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Welsh KJ, Patel CB, Fernando RC, Torres JD, Medrek SK, Schnapp WB, et al.. Prevalence of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia in houston outreach medicine, education, and social services (HOMES) clinic patients: Implications for student-managed clinics for underserved populations. Academic Medicine. 2012;87: 656–661. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e31824d4540 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsuang MT, Dempsey GM, Dvoredsky A, Struss A. A family history study of schizo affective disorder. Biological Psychiatry. 1977;12: 331–338. - PubMed

