Immunopathophysiology of human sepsis
- PMID: 36470832
- PMCID: PMC9783164
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104363
Immunopathophysiology of human sepsis
Abstract
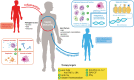
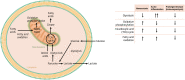
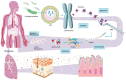
Sepsis is an ill-defined syndrome yet is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The most recent consensus defines sepsis as life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection. However, this definition belies the complexity and breadth of immune mechanisms involved in sepsis, which are characterized by simultaneous hyperinflammation and immune suppression. In this review, we describe the immunopathogenesis of sepsis and highlight some recent pathophysiological findings that have expanded our understanding of sepsis. Sepsis endotypes can be used to divide sepsis patients in different groups with distinct immune profiles and outcomes. We also summarize evidence on the role of the gut microbiome in sepsis immunity. The challenge of the coming years will be to translate our increasing knowledge about the molecular mechanisms underlying sepsis into therapies that improve relevant patient outcomes.
Keywords: Hyperinflammation; Immune suppression; Pathogenesis; Sepsis.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- van der Poll T., Shankar-Hari M., Wiersinga W.J. The immunology of sepsis. Immunity. 2021;54(11):2450–2464. - PubMed
-
- van der Poll T., Wiersinga W.J. In: Principles and practice of infectious diseases. 9th ed. Mandell D., Bennett, editors. Saunders; 2019. Chapter 73: sepsis and septic shock.
-
- Torres L.K., Pickkers P., van der Poll T. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression. Annu Rev Physiol. 2022;84:157–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

