Mutation of the polyadenylation complex subunit CstF77 reveals that mRNA 3' end formation and HSP101 levels are critical for a robust heat stress response
- PMID: 36472129
- PMCID: PMC9940869
- DOI: 10.1093/plcell/koac351
Mutation of the polyadenylation complex subunit CstF77 reveals that mRNA 3' end formation and HSP101 levels are critical for a robust heat stress response
Abstract
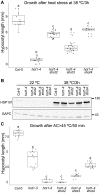
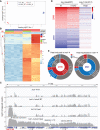
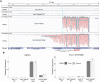
Heat shock protein 101 (HSP101) in plants, and bacterial and yeast orthologs, is essential for thermotolerance. To investigate thermotolerance mechanisms involving HSP101, we performed a suppressor screen in Arabidopsis thaliana of a missense HSP101 allele (hot1-4). hot1-4 plants are sensitive to acclimation heat treatments that are otherwise permissive for HSP101 null mutants, indicating that the hot1-4 protein is toxic. We report one suppressor (shot2, suppressor of hot1-4 2) has a missense mutation of a conserved residue in CLEAVAGE STIMULATION FACTOR77 (CstF77), a subunit of the polyadenylation complex critical for mRNA 3' end maturation. We performed ribosomal RNA depletion RNA-Seq and captured transcriptional readthrough with a custom bioinformatics pipeline. Acclimation heat treatment caused transcriptional readthrough in hot1-4 shot2, with more readthrough in heat-induced genes, reducing the levels of toxic hot1-4 protein and suppressing hot1-4 heat sensitivity. Although shot2 mutants develop like the wild type in the absence of stress and survive mild heat stress, reduction of heat-induced genes and decreased HSP accumulation makes shot2 in HSP101 null and wild-type backgrounds sensitive to severe heat stress. Our study reveals the critical function of CstF77 for 3' end formation of mRNA and the dominant role of HSP101 in dictating the outcome of severe heat stress.
© American Society of Plant Biologists 2022. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

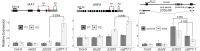

Similar articles
-
Mutations in an Arabidopsis mitochondrial transcription termination factor-related protein enhance thermotolerance in the absence of the major molecular chaperone HSP101.Plant Cell. 2012 Aug;24(8):3349-65. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.101006. Epub 2012 Aug 31. Plant Cell. 2012. PMID: 22942382 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp101 is necessary for heat tolerance but dispensable for development and germination in the absence of stress.Plant J. 2001 Jul;27(1):25-35. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01066.x. Plant J. 2001. PMID: 11489180
-
Mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana defective in the acquisition of tolerance to high temperature stress.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Apr 11;97(8):4392-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.8.4392. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10760305 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between heat shock proteins HSP101 and HSA32 prolongs heat acclimation memory posttranscriptionally in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2013 Apr;161(4):2075-84. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.212589. Epub 2013 Feb 25. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23439916 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis reveals domain interactions of Arabidopsis Hsp100/ClpB and cooperation with the small heat shock protein chaperone system.Plant Cell. 2005 Feb;17(2):559-71. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.027540. Epub 2005 Jan 19. Plant Cell. 2005. PMID: 15659638 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Revisiting CPSF30-mediated alternative polyadenylation in Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS One. 2025 Feb 24;20(2):e0319180. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319180. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39992955 Free PMC article.
-
Host genotype, soil composition, and geo-climatic factors shape the fonio seed microbiome.Microbiome. 2024 Jan 17;12(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01725-5. Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 38233870 Free PMC article.
-
A CPF-like phosphatase module links transcription termination to chromatin silencing.Mol Cell. 2024 Jun 20;84(12):2272-2286.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.05.016. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38851185 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-mRNA processing factors differentially impact coordination between co-transcriptional cleavage and transcription termination.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 1;16(1):7086. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62555-7. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40750766 Free PMC article.
-
Natural variation in the plant polyadenylation complex.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jan 22;14:1303398. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1303398. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38317838 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreassi C, Riccio A (2009) To localize or not to localize: mRNA fate is in 3′UTR ends. Trends Cell Biol 19(9): 465–474 - PubMed
-
- Antosz W, Pfab A, Ehrnsberger HF, Holzinger P, Köllen K, Mortensen SA, Bruckmann A, Schubert T, Längst G, Griesenbeck J, et al. (2017) The composition of the Arabidopsis RNA polymerase II transcript elongation complex reveals the interplay between elongation and mRNA processing factors. Plant Cell 29(4): 854–870 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai Y, Auperin TC, Chou C-Y, Chang G-G, Manley JL, Tong L (2007) Crystal structure of murine CstF-77: dimeric association and implications for polyadenylation of mRNA precursors. Mol Cell 25(6): 863–875 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

