The tree of blobs of a species network: identifiability under the coalescent
- PMID: 36472708
- PMCID: PMC10062380
- DOI: 10.1007/s00285-022-01838-9
The tree of blobs of a species network: identifiability under the coalescent
Abstract
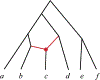
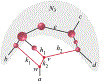
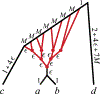
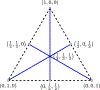
Inference of species networks from genomic data under the Network Multispecies Coalescent Model is currently severely limited by heavy computational demands. It also remains unclear how complicated networks can be for consistent inference to be possible. As a step toward inferring a general species network, this work considers its tree of blobs, in which non-cut edges are contracted to nodes, so only tree-like relationships between the taxa are shown. An identifiability theorem, that most features of the unrooted tree of blobs can be determined from the distribution of gene quartet topologies, is established. This depends upon an analysis of gene quartet concordance factors under the model, together with a new combinatorial inference rule. The arguments for this theoretical result suggest a practical algorithm for tree of blobs inference, to be fully developed in a subsequent work.
Keywords: Network multispecies coalescent model; Phylogenetics; Phylogenomics; Species network; Tree of blobs.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Figures
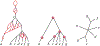
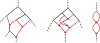
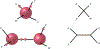
Similar articles
-
TINNiK: inference of the tree of blobs of a species network under the coalescent model.Algorithms Mol Biol. 2024 Nov 5;19(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13015-024-00266-2. Algorithms Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39501362 Free PMC article.
-
TINNiK: Inference of the Tree of Blobs of a Species Network Under the Coalescent.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 24:2024.04.20.590418. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.20.590418. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Algorithms Mol Biol. 2024 Nov 5;19(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13015-024-00266-2. PMID: 38712257 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Identifiability of species network topologies from genomic sequences using the logDet distance.J Math Biol. 2022 Apr 7;84(5):35. doi: 10.1007/s00285-022-01734-2. J Math Biol. 2022. PMID: 35385988 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges in Species Tree Estimation Under the Multispecies Coalescent Model.Genetics. 2016 Dec;204(4):1353-1368. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.190173. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27927902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implementing and testing the multispecies coalescent model: A valuable paradigm for phylogenomics.Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2016 Jan;94(Pt A):447-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2015.10.027. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2016. PMID: 26518740 Review.
Cited by
-
TINNiK: inference of the tree of blobs of a species network under the coalescent model.Algorithms Mol Biol. 2024 Nov 5;19(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13015-024-00266-2. Algorithms Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39501362 Free PMC article.
-
Identifiability of Level-1 Species Networks from Gene Tree Quartets.Bull Math Biol. 2024 Jul 25;86(9):110. doi: 10.1007/s11538-024-01339-4. Bull Math Biol. 2024. PMID: 39052074 Free PMC article.
-
NANUQ+: A divide-and-conquer approach to network estimation.Algorithms Mol Biol. 2025 Jul 25;20(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13015-025-00274-w. Algorithms Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40713832 Free PMC article.
-
TINNiK: Inference of the Tree of Blobs of a Species Network Under the Coalescent.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 24:2024.04.20.590418. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.20.590418. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Algorithms Mol Biol. 2024 Nov 5;19(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13015-024-00266-2. PMID: 38712257 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
IDENTIFIABILITY OF LEVEL-1 SPECIES NETWORKS FROM GENE TREE QUARTETS.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 11:arXiv:2401.06290v1. ArXiv. 2024. Update in: Bull Math Biol. 2024 Jul 25;86(9):110. doi: 10.1007/s11538-024-01339-4. PMID: 38259350 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Allman ES, Degnan JH, Rhodes JA (2011) Identifying the rooted species tree from the distribution of unrooted gene trees under the coalescent. J Math Biol 62(6):833–862 - PubMed
-
- Allman ES, Matias C, Rhodes JA (2009) Identifiability of parameters in latent structure models with many observed variables. Ann Stat 37(6A):3099–3132
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

