Association of Type 2 Diabetes Subgroups With Cognitive Status Without Modification From Lifestyle Intervention
- PMID: 36472933
- PMCID: PMC10413427
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgac706
Association of Type 2 Diabetes Subgroups With Cognitive Status Without Modification From Lifestyle Intervention
Abstract
Context: Type 2 diabetes is a risk factor for incident dementia but whether risk and treatment/prevention strategies differ by diabetes subgroup is unknown.
Objective: We assessed (1) whether specific type 2 diabetes (T2D) subgroups are associated with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or probable dementia (PD), and (2) whether T2D subgroups modified the association of the Action for Health in Diabetes (Look AHEAD) multidomain intensive lifestyle intervention (ILI) with MCI/PD.
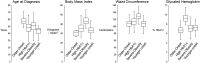
Methods: We included 3760 Look AHEAD participants with T2D and overweight or obesity randomly assigned to 10 years of ILI or diabetes support and education. We used k-means clustering techniques with data on age of diabetes diagnosis, body mass index, waist circumference, and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) to characterize diabetes subgroups at randomization. Prevalent MCI/PD were centrally adjudicated based on standardized cognitive tests and other health information 10 to 13 years after randomization. We estimated marginal probabilities for prevalent MCI/PD among T2D subgroups with adjustment for potential confounders and attrition and examined whether ILI modified any associations.
Results: Four distinct T2D subgroups were identified, characterized by older age at diabetes onset (43% of sample), high HbA1c (13%), severe obesity (23%), and younger age at onset (22%). Unadjusted prevalence of MCI/PD (314 cases, 8.4%) differed across T2D subgroup (older onset = 10.5%, severe obesity = 9.0%, high HbA1c = 7.9%, and younger onset = 4.0%). Adjusted probability for MCI/PD within T2D subgroup was highest for the severe obesity subgroup and lowest for the younger onset subgroup but did not differ by ILI arm (interaction P value = 0.84).
Conclusions: Among individuals with T2D and overweight or obesity, probability of MCI/PD differed by T2D subgroup. Probability of MCI/PD was highest for a subgroup characterized by severe obesity.
Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT00017953.
Keywords: intensive lifestyle intervention; mild cognitive status and probable dementia; type 2 diabetes subgroups.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Xue M, Xu W, Ou YN, et al. . Diabetes mellitus and risks of cognitive impairment and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 144 prospective studies. Ageing Res Rev. 2019;55:100944. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- K99 AG065419/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057151/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057136/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057002/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK036836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057177/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057078/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001346/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK048520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057135/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG065419/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK046204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR002719/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057219/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057178/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072947/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States