Transglutaminase Activities of Blood Coagulant Factor XIII Are Dependent on the Activation Pathways and on the Substrates
- PMID: 36473493
- PMCID: PMC10719020
- DOI: 10.1055/a-1993-4193
Transglutaminase Activities of Blood Coagulant Factor XIII Are Dependent on the Activation Pathways and on the Substrates
Abstract
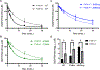
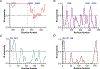
Factor XIII (FXIII) catalyzes formation of γ-glutamyl-ε-lysyl crosslinks between reactive glutamines (Q) and lysines (K). In plasma, FXIII is activated proteolytically (FXIII-A*) by the concerted action of thrombin and Ca2+. Cellular FXIII is activated nonproteolytically (FXIII-A°) by elevation of physiological Ca2+ concentrations. FXIII-A targets plasmatic and cellular substrates, but questions remain on correlating FXIII activation, resultant conformational changes, and crosslinking function to different physiological substrates. To address these issues, the characteristics of FXIII-A* versus FXIII-A° that contribute to transglutaminase activity and substrate specificities were investigated. Crosslinking of lysine mimics into a series of Q-containing substrates were measured using in-gel fluorescence, mass spectrometry, and UV-Vis spectroscopy. Covalent incorporation of fluorescent monodansylcadaverine revealed that FXIII-A* exhibits greater activity than FXIII-A° toward Q residues within Fbg αC (233-425 WT, Q328P Seoul II, and Q328PQ366N) and actin. FXIII-A* and FXIII-A° displayed similar activities toward α2-antiplasmin (α2AP), fibronectin, and Fbg αC (233-388, missing FXIII-binding site αC 389-402). Furthermore, the N-terminal α2AP peptide (1-15) exhibited similar kinetic properties for FXIII-A* and FXIII-A°. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry assays with glycine ethyl ester and Fbg αC (233-425 WT, αC E396A, and truncated αC (233-388) further documented that FXIII-A* exerts greater benefit from the αC 389-402 binding site than FXIII-A°. Conformational properties of FXIII-A* versus A° are proposed to help promote transglutaminase function toward different substrates. A combination of protein substrate disorder and secondary FXIII-binding site exposure are utilized to control activity and specificity. From these studies, greater understandings of how FXIII-A targets different substrates are achieved.
Thieme. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures




References
-
- Richardson VR, Cordell P, Standeven KF, Carter AM. Substrates of Factor XIII-A: roles in thrombosis and wound healing. Clin Sci (Lond). 2013;124(3):123–37 - PubMed
-
- Schroeder V, Kohler HP. Factor XIII: Structure and Function. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2016;42(4):422–8 - PubMed
-
- Muszbek L, Bereczky Z, Bagoly Z, Komaromi I, Katona E. Factor XIII: a coagulation factor with multiple plasmatic and cellular functions. Physiol Rev. 2011;91(3):931–72 - PubMed
-
- Mitchell JL, Mutch NJ. Let’s cross-link: diverse functions of the promiscuous cellular transglutaminase factor XIII-A. J Thromb Haemost. 2019;17(1):19–30 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

