Experimental VX2 Rabbit Liver Tumor Model in Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Cirrhosis of the Liver
- PMID: 36473611
- PMCID: PMC11037556
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2022.11.026
Experimental VX2 Rabbit Liver Tumor Model in Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Cirrhosis of the Liver
Abstract
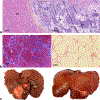
Liver cirrhosis is a major underlying factor in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Currently, there is an unmet need for midsize experimental vertebrate models that would offer reproducible implantable liver tumors in a cirrhotic liver background. This study establishes a protocol for a syngeneic rabbit model of VX2 liver cancer with underlying liver cirrhosis induced using carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). Male New Zealand white rabbits (n = 3) received CCl4 by intragastric administration once weekly. Concentrations started at 5% v/v CCl4 dissolved in olive oil. CCl4 dosing was progressively increased every week by 2.5% v/v increments for the duration of treatment (16 weeks total). VX2 tumors were then orthotopically implanted into the left hepatic lobe and allowed to grow for 3 weeks. Cross-sectional imaging confirmed the presence of hepatic tumors. Gross and histopathological evaluations showed reproducible tumor growth in the presence of liver cirrhosis in all animals.
Copyright © 2022 SIR. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the other authors have identified a conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

