Discovery and systematic characterization of risk variants and genes for coronary artery disease in over a million participants
- PMID: 36474045
- PMCID: PMC9729111
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-022-01233-6
Discovery and systematic characterization of risk variants and genes for coronary artery disease in over a million participants
Abstract
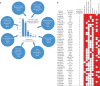
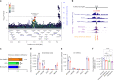
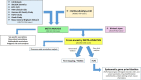
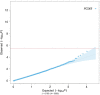
The discovery of genetic loci associated with complex diseases has outpaced the elucidation of mechanisms of disease pathogenesis. Here we conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) for coronary artery disease (CAD) comprising 181,522 cases among 1,165,690 participants of predominantly European ancestry. We detected 241 associations, including 30 new loci. Cross-ancestry meta-analysis with a Japanese GWAS yielded 38 additional new loci. We prioritized likely causal variants using functionally informed fine-mapping, yielding 42 associations with less than five variants in the 95% credible set. Similarity-based clustering suggested roles for early developmental processes, cell cycle signaling and vascular cell migration and proliferation in the pathogenesis of CAD. We prioritized 220 candidate causal genes, combining eight complementary approaches, including 123 supported by three or more approaches. Using CRISPR-Cas9, we experimentally validated the effect of an enhancer in MYO9B, which appears to mediate CAD risk by regulating vascular cell motility. Our analysis identifies and systematically characterizes >250 risk loci for CAD to inform experimental interrogation of putative causal mechanisms for CAD.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All deCODE affiliated authors are employees of deCODE/Amgen. The TIMI Study Group has received institutional research grant support through Brigham and Women’s from Abbott, Amgen, Aralez, AstraZeneca, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, BRAHMS, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, GlaxoSmithKline, Intarcia, Janssen, MedImmune, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Poxel, Quark Pharmaceuticals, Roche, Takeda, The Medicines Company, and Zora Biosciences. R.C., J.C.H., M.I. and F.M. work at the Clinical Trial Service Unit and Epidemiological Studies Unit, Nuffield Department of Population Health, which receives research grants from industry that are governed by the University of Oxford contracts that protect its independence and has a staff policy of not taking personal payments from industry; further details can be found at
Figures



Comment in
-
Finding causal genes underlying risk for coronary artery disease.Nat Genet. 2022 Dec;54(12):1768-1769. doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01094-z. Nat Genet. 2022. PMID: 36474046 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MR/L003120/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/S502443/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BRC-1215-20014/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- R01 HL125863/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/14/5/30893/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- SP/13/2/30111/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- SP/16/4/32697/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL146860/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- FS/14/55/30806/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- SP/19/2/34462/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- K08 HG010155/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL109946/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 DK105554/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR002542/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201700004C/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 203141/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- FS/14/66/3129/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135824/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/18/13/33946/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- T32 HG000040/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RE/13/1/30181/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- K08 HL153950/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700002C/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201700002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL153937/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/13/13/30194/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- T32 HL007604/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- SP/09/002/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G0800270/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

