Knockdown of lncRNA XIST Ameliorates IL-1 β-Induced Apoptosis of HUVECs and Change of Tissue Factor Level via miR-103a-3p/HMGB1 Axis in Deep Venous Thrombosis by Regulating the ROS/NF- κ B Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 36474713
- PMCID: PMC9699739
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6256384
Knockdown of lncRNA XIST Ameliorates IL-1 β-Induced Apoptosis of HUVECs and Change of Tissue Factor Level via miR-103a-3p/HMGB1 Axis in Deep Venous Thrombosis by Regulating the ROS/NF- κ B Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Background: The effect of lncRNA X inactive-specific transcript (XIST) inducing cardiovascular diseases on deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and its mechanism has not been reported. In this study, we uncovered the mystery that lncRNA XIST causes DVT with HUVEC dysfunction.
Method: The expression levels of lncRNA XIST and miR-103a-3p were detected by qRT-PCR, and HMGB1 expression was determined by qRT-PCR and western blot. The correlations among the expression levels of lncRNA XIST, miR-103a-3p, and HMGB1 were determined by Spearman's rank-order correlation test. XIST siRNA (si-XIST) was transfected into HUVECs to knock down the intrinsic expression of lncRNA XIST. The influences of si-XIST on interleukin-1 beta- (IL-1β-) treated HUVEC viability and apoptosis and the level of tissue factor (TF) were detected by MTT, flow cytometry, and ELISA kit, respectively. The relationships between lncRNA XIST, miR-103a-3p, and HMGB1 were predicted by the Encyclopedia of RNA Interactomes (ENCORI) database and verified by dual luciferase reporter assay. The effects of lncRNA XIST and miR-103a-3p on HMGB1 expression were detected by qRT-PCR, western blot, and immunofluorescence analysis. The levels of ROS/NF-κB pathway-related proteins were detected to study the regulatory mechanism of lncRNA XIST/miR-103a-3p/HMGB1 on IL-1β-treated HUVECs apoptosis and change of TF level.
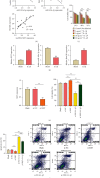
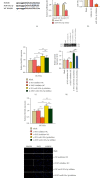
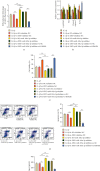
Results: The upregulated expression levels of lncRNA XIST and HMGB1 and downregulated level of miR-103a-3p were found in the plasma of DVT patients and IL-1β-treated HUVECs. Si-XIST promoted cell viability and inhibited HUVEC apoptosis and ameliorated the change of TF level triggered by IL-1β. lncRNA XIST sponged miR-103a-3p and miR-103a-3p targeted HMGB1. Si-XIST inhibited the ROS/NF-κB pathway to suppress HUVEC apoptosis and ameliorate the change of TF level induced by IL-1β via the miR-103a-3p/HMGB1 axis.
Conclusion: lncRNA XIST sponged miR-103a-3p improving HMGB1 expression to exacerbate DVT by activating the ROS/NF-κB signaling pathway. Our findings indicated that lncRNA XIST can be used as a potential therapeutic target in DVT.
Copyright © 2022 Guangxin Cao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Patterson B. O., Hinchliffe R., Loftus I. M., Thompson M. M., Holt P. J. E. Indications for catheter-directed thrombolysis in the management of acute proximal deep venous thrombosis. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology . 2010;30(4):669–674. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.200766. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

